Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
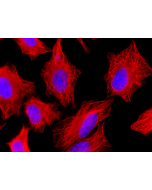
anti-Tubulin (glycylated), pAb (Gly-pep1)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Polyclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to D431EQGEFE(G-COOH*)EEEG441-NH2 of human Tubulin β-2A chain (*secondary glycine branched from γ-carboxyl group of glutamate as isopeptide bond). |
| Application |
Western Blot: (1:10'000) |
| Crossreactivity |
Dog Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
This antibody recognizes mono or bi-glycylated Tubulins. The activity of glycylating enzymes (TTLL3 and TTLL8) in cultured cells leads mainly to the modification of α- and β-tubulin, but also of other, yet unidentified protein substrates also detected by the antibody Gly-pep1. In immunofluorescence labeling, the antibody strongly labels glycylated microtubules. As glycylation of microtubules is particularly found in cilia and flagella, Gly-pep1 labels motile cilia as well as some (mostly very long) primary cilia (see paper S. Gadadhar, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 216, 2701 (2017) for more details). |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Epitope-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Accession Number | Q13885 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Microtubules are key cytoskeletal elements that are found in all eukaryotic cells. Microtubules fulfil a large range of different functions, which are thought to be controlled by the ‘tubulin code’ – mechanism to generate distinct microtubule identities. One mechanism to label specific microtubules are tubulin posttranslational modifications (PTMs), of which a large variety exists. One of these modifications is glycylation, which is generated by the addition of secondary (branched) glycine chains to the main (primary) peptide chain of the protein. The length of these branch chains can vary from one to more than 20 glycine residues. Glycylation is catalysed by the enzymes TTLL3, TTLL8 and TTLL10 from the tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) family. Especially TTLL3 and TTLL8 are essential for the initiation of the glycylation because the generate the nascent glycine chain.
The Gly-pep1 antibody was raised against a peptide mimicking beta2-tubulin (TUBB2A) with a single glycine branch on E437. The antibody specifically detects glycylated tubulin, and also other yet unknown glycylation substrates in cells as well as in tissues. As glycylation of microtubules is particularly found in cilia and flagella, Gly-pep1 labels motile cilia as well as primary cilia (Gadadhar et al., 2017)
- Tubulin glycylation controls primary cilia length: S. Gadadhar, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 216, 2701 (2017)
- Tubulin glycylation controls axonemal dynein activity, flagellar beat, and male fertility: S. Gadadhar, et al.; Science 371, eabd4914 (2021)
- Proteomic analysis of Giardia lamblia and Trichomonas vaginalis flagella reveal unique post-translational modifications in tubulin that provide clues to regulation of their motilities: A. Sudhakar, et al.; Proteomics e2100004 (2021)