Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
IL-33 (oxidation resistant) (human) (rec.) (untagged)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | IL-33 (human) (C208S/C232S Mutant); Interleukin-33 (human) (C208S/C232S Mutant); IL-1F11; NF-HEV |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | E. coli |
| Sequence |
Human IL-33 (aa 112-270) is untagged. Amino acids C208 and C232 have been mutated to serine to protect IL-33 from oxidation. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Specificity |
Binds to human and mouse ST2. |
| Biological Activity |
Activates human and mouse ST2-dependent NF-κB pathway. Activates in vivo Innate Lymphoid Cells 2 (ILC2) at 0.4µg /ml. |
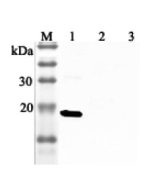
| MW | ~17kDa (SDS-PAGE); Monomer (Size Exclusion Chromatography) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Concentration |
After reconstitution: for 10µg size: 0.1mg/ml for 100µg size: 1mg/ml |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 100μl sterile water. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS + 1mM DTT |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link Q2YEJ5: Interleukin-33 (human) |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. PBS containing at least 0.1% BSA should be used for further dilutions. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Interleukin-33 (IL-33; HF-NEV; IL-1F11), a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, is expressed by many cell types following pro-inflammatory stimulation and is thought to be released upon cell lysis. IL-33 binds to and signals through ST2 (IL-1R1) and its stimulation recruits MYD88, IRAK, IRAK4 and TRAF6, followed by phosphorylation of ERK1 (MAPK3) / ERK2 (MAPK1), p38 (MAPK14) and JNK. The ability of IL-33 to target numerous immune cell types, like Th2-like cells, mast cells and B1 cells, and to induce cytokine and chemokine production underlines its potential in influencing the outcome of a wide range of diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, atopic allergy & anaphylaxis, cardiovascular disease/atherosclerosis, nervous system diseases and sepsis. IL-33 facilitates Treg expansion in vitro and in vivo. Recently, IL-33 has been involved in adipocyte differentiation. The biological activity of IL-33 at its receptor ST2 is rapidly terminated in the extracellular environment by its oxidation (formation of two disulfide bridges), resulting in an extensive conformational change that disrupts the ST2 binding site. Mutations at amino acids C208S/C232S protect IL-33 from oxidation and increase its activity.
- Oxidation of the alarmin IL-33 regulates ST2-dependent inflammation: E.S. Cohen, et al.; Nat. Commun. 6, ID8327 (2015)
- Tumour-derived PGD2 and NKp30-B7H6 engagement drives an immunosuppressive ILC2-MDSC axis: S. Trabanelli, et al.; Nat. Commun. 8, 593 (2017)
- Tissue cytokine IL-33 modulates the cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocyte activity during nutrient deprivation by regulation of lineage-specific differentiation programs: C. Dreis, et al.; Front. Immunol. 10, 1698 (2019)
- Long-Acting IL-33 Mobilizes High-Quality Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells More Efficiently Than Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor or AMD3100: C. Alt, et al.; Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant 25, 1475 (2019)
- PPARɣ drives IL-33-dependent ILC2 pro-tumoral functions: G. Ercolano, et al.; Nat. Commun. 12, 2538 (2021)