Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
CD152 [CTLA-4] (human) (rec.) (untagged)
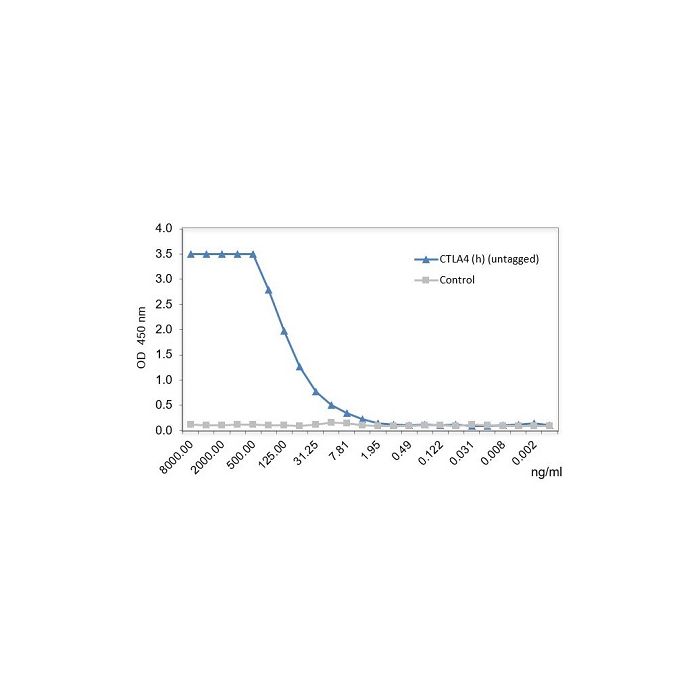
Method: CD152 [CTLA-4] (human) (rec.) (untagged) is coated on an ELISA plate at 1 μg/ml overnight at 4°C. CD80 (human):Fc (mouse) (rec.) (blue line) or a control mouse Fc (Prod. No. AG-35B-0008) (grey line) is incubated (starting at a concentration of 8,000 ng/ml with a twofold serial dilution) during one hour at RT and the interaction is then detected using a goat anti-mouse-(HRP).
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated Antigen 4; Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Protein 4 |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | HEK 293 cells |
| Sequence |
Human CD152 [CTLA-4] (aa 36-161) is untagged. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Biological Activity |
Binds to human CD80. |
| MW | ~18kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test). |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml after reconstitution. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute with 50µl endotoxin-free water. |
| Accession Number | P16410 |
| Formulation | Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Other Product Data |
UniProt link P16410: CD152 /CTLA4 (human) Protein |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After opening, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
CD152 (Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; CTLA-4) is an inhibitory receptor belonging to the CD28 immunoglobulin subfamily, expressed primarily by T cells. Its ligands, CD80 and CD86, are typically found on the surface of antigen-presenting cells and can either bind CD28 or CTLA-4, resulting in a costimulatory or a co-inhibitory response, respectively. Because of its dampening effect, CTLA-4 is a crucial regulator of T cell homeostasis and self-tolerance.
While CD28 promotes T cell activation and proliferation, CTLA-4 is reported to dampen T cell responses through a variety of mechanisms. Prior to activation, conventional T cells (Tconv) express low levels of CTLA-4, predominantly in intracellular compartments. Upon activation, CTLA-4 expression is upregulated and becomes increasingly detectable on the cell surface. In Tregs on the other hand, transmembrane CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed and plays an important role in Treg homeostasis and function. In general, T cell CTLA-4 is largely constrained to intracellular expression although some surface expression may be detectable owing to the rapid, continuous shuttling of CTLA-4 between intracellular compartments and the plasma membrane.
Recently, CTLA-4 has been studied in dendritic cells and tumors, showing that CTLA-4 plays nonredundant and critical roles in thymic development, T cell priming, peripheral tolerance, and a variety of other critical immunoregulatory functions as an immune checkpoint in Immuno-oncology research.






![CD152 [CTLA-4] (human) (rec.) (His)](https://update.adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/cache/9c281c7ec96bf9060309dac73f492a03/a/g/ag-40b-0228-binding_assay-400px.jpg)
![CD152 [CTLA-4] (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (non-lytic)](https://update.adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/adipogen_logo_bw_3.png)