Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
EnhancedFasL, Soluble (human) (rec.) Pack

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | APO-1L; CD95L; CD178; TNFSF 6; Fas Ligand |
| Product Type | Set |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Compound Screening |
| Specificity |
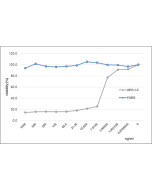
Binds to human and mouse Fas (CD95; APO-1). Induces apoptosis of human Jurkat T cells at a concentration of <1ng/ml. |
| Crossreactivity |
Human Mouse |
| Kit Contains |
1 Set |
| Other Product Data |
Source/Host: |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 6 months after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
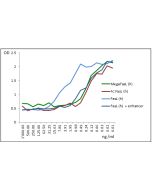
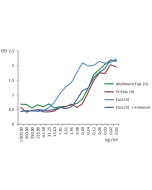
FasL, Soluble (human) (rec.) induces apoptosis in a concentration range of <1ng/ml in the presence of 0.1 to 1µg/ml of TNF Ligands Enhancer (Prod. No. AG-35B-0001). (Optimal conditions must be determined individually for each cell line tested)
- Activation of Fas by FasL induces apoptosis by a mechanism that cannot be blocked by Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L): D.C. Huang, et al.; PNAS 96, 14871 (1999)
- Fas ligand-induced c-Jun kinase activation in lymphoid cells requires extensive receptor aggregation but is independent of DAXX, and Fas-mediated cell death does not involve DAXX, RIP, or RAIDD: A. Villunger, et al.; J. Immunol. 165, 1337 (2000)
- Fas engagement induces the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs), the release of interleukin (IL)-1beta, and the production of interferon gamma in the absence of IL-12 during DC-T cell cognate interaction: a new role for Fas ligand in inflammatory responses: M. Rescigno, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 192, 1661 (2000)
- NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP: O. Micheau, et al.; Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 5299 (2001)
- Potentiation of Fas-mediated apoptosis by an engineered glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked Fas: P. Legembre, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 9, 329 (2002)
- Multiple pathways of TWEAK-induced cell death: M. Nakayama, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 734 (2002)
- Innate direct anticancer effector function of human immature dendritic cells. II. Role of TNF, lymphotoxin-alpha(1)beta(2), Fas ligand, and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand: G. Lu, et al.; J. Immunol. 168, 1831 (2002)
- Induction of apoptosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells by activation of the Fas (Apo-1/CD95) death-signal pathway: J.H. 4th Stewart et al.; J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 123, 295 (2002)
- Hepatic natural killer cells exclusively kill splenic/blood natural killer-resistant tumor cells by the perforin/granzyme pathway: D. Vermijlen, et al.; J. Leukoc. Biol. 72, 668 (2002)
- Caspase-10 is recruited to and activated at the native TRAIL and CD95 death-inducing signalling complexes in a FADD-dependent manner but can not functionally substitute caspase-8: M.R. Sprick, et al.; EMBO J. 21, 4520 (2002)
- An essential role for membrane rafts in the initiation of Fas/CD95-triggered cell death in mouse thymocytes: A.O. Hueber, et al.; EMBO Rep. 3, 190 (2002)
- Cutting edge: SDS-stable Fas microaggregates: an early event of Fas activation occurring with agonistic anti-Fas antibody but not with Fas ligand: P. Legembre, et al.; J. Immunol. 171, 5659 (2003)
- The role of p53 and Fas in a model of acute murine graft-versus-host disease: S. Yada, et al.; J. Immunol. 174, 1291 (2005)
- CD1d-unrestricted human NKT cells release chemokines upon Fas engagement: M. Giroux & F. Denis; Blood 105, 703 (2005)
- Amplification of CD95 activation by caspase 8-induced endosomal acidification in rat hepatocytes: R. Reinehr, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 283, 2211 (2008)






![CD95 [Fas] (human)-huIg Fusion Protein (preservative free)](https://update.adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/adipogen_logo_bw_3.png)