Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
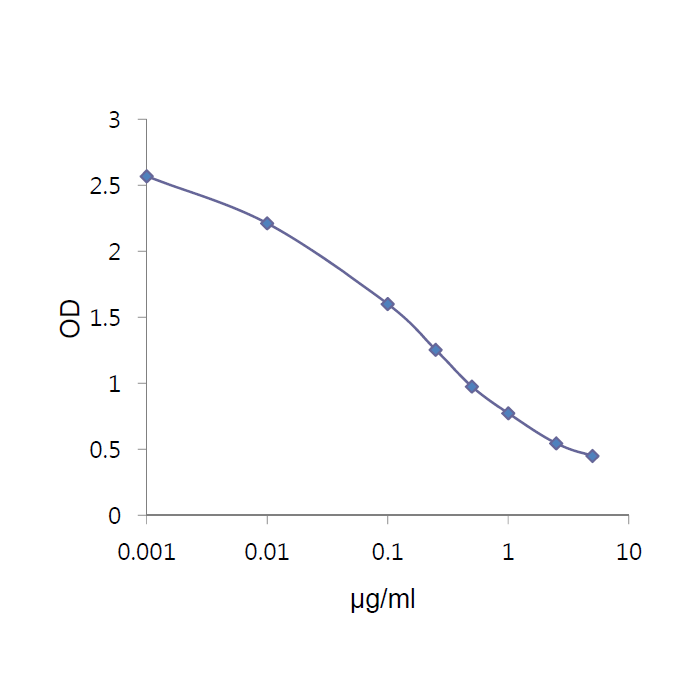
RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Retinol Binding Protein 4 |
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Detects human RBP4. Does not cross-react with human adiponectin, human resistin or human RELM-β. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Quantity | 1 x 96 wells |
| Sensitivity | 1ng/ml |
| Range | 0.001 to 5μg/ml |
| Sample Type |
Cell Culture Supernatant Plasma Serum Urine |
| Assay Type | Competitive |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
After standard reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Plate and reagents should reach room temperature before use. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4; RBP) is a 21kDa secreted protein, a member of the lipocalin family and is known as the primary transporter of retinol (vitamin A) to tissues. A recent report revealed RBP4 as an adipokine linking glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) suppression in adipose tissue to insulin. Elevated human and mouse serum RBP4 levels are associated with insulin resistance and its severity, obesity and certain components of metabolic syndrome. Furthermore, human serum RBP4 levels are closely related to renal function and recent studies have shown an association between serum RBP4 levels and urinary albumin excretion. The urinary RBP4 concentration may be a valuable marker for both, insulin resistance and microalbuminuria in insulin-resistant subjects.
- Retinol-binding protein 4 in human obesity: J. Janke, et al.; Diabetes 55, 2805 (2006)
- Plasma retinol-binding protein-4 concentrations are elevated in human subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes: Y.M. Cho, et al.; Diabetes Care 29, 2457 (2006)
- Association of serum retinol binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in apparently healthy adolescents: D.C. Lee et al.; Metab. Clin. Exp. 56, 327 (2007)
- High circulating retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with elevated liver fat, but not with total-, subcutaneous-, visceral-, or intramyocellular fat in humans: N. Stefan et al.; Diabetes Care 30, 1173 (2007)
- Retinol-binding protein 4 as a plasma biomarker of renal dysfunction and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A. Cabre, et al.; J. Intern. Med. 262, 496 (2007)
- Visceral adiposity is associated with serum retinol binding protein-4 levels in healthy women: J.W. Lee, et al.; Obesity (Silver Spring) 15, 2225 (2007)
- Circulating retinol-binding protein-4, insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and insulin disposition index in obese and nonobese subjects: response to Broch et al: N. Stefan, et al.; Diabetes Care 30, e91 (2007)
- Insulin resistance is unrelated to circulating retinol binding protein and protein C inhibitor: M. Promintzer, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92, 4306 (2007)
- Serum levels of adipokine retinol-binding protein-4 in relation to renal function: M. Ziegelmeier, et al.; Diabetes Care 30, 2588 (2007)
- Serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels are elevated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: J.A. Seo, et al.; Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf ) 68, 555 (2008)
- Retinol binding protein-4 elevation is associated with serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level independently of obesity in elderly subjects with normal glucose tolerance: S. H. Choi, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 2313 (2008)
- Retinol binding protein 4 concentrations are influenced by renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: T. Masaki, et al.; Metabolism 57, 1340 (2008)
- High plasma retinol binding protein-4 and low plasma adiponectin concentrations are associated with severity of glucose intolerance in women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus: S.H. Choi, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 3142 (2008)
- Decreased clearance of serum retinol-binding protein and elevated levels of transthyretin in insulin-resistant ob/ob mice: N. Mody, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E785 (2008)
- Identification of serum biomarkers in brain-injured adults- potential for predicting elevated intracranial pressure: G. Hergenroeder, et al.; J. Neurotrauma 25, 79 (2008)
- Retinol binding protein 4: a new marker of virus-induced steatosis in patients infected with Hepatitis C virus genotype 1: S. Petta, et al.; Hepatology 48, 28 (2008)
- Insulin-Sensitizing Effects of Exercise on Adiponectin and Retinol-Binding Protein-4 Concentrations in Young and Middle-Aged Women: S. Lim, et al.; J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 2263 (2008)
- Circulating retinol-binding protein-4 concentration might reflect insulin resistance-associated iron overload: J.M. Fernández-Real, et al.; Diabetes 57, 1918 (2008)
- Association between serum retinol-binding protein 4 and small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in young adult women: S. Usui, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta 399, 45 (2009)
- Serum Adipocyte Fatty Acid–Binding Protein Levels Are Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: J.H. Koh, et al.; Diabetes Care 32, 147 (2009)
- Elevated serum g-glutamyltransferase levels are independently associated with insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects: J.Y. Shin, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 84, 152 (2009)
- Clinical Implications of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Asthmatic Children: Y.H. Park, et al.; J. Korean Med. Sci. 24, 1010 (2009)
- Effect of exercise training on A-FABP, lipocalin-2 and RBP4 levels in obese women: K.M. Choi, et al.; Clin. Endocrinol. 70, 569 (2009)
- Circuit resistance exercise improves glycemic control and adipokines in females with type 2 diabetes mellitus: S. Kang, et al.; JSSM 8, 682 (2009)
- Visceral Obesity is Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome and Elevated Plasma Retinol Binding Protein-4 Level in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: S. Makino, et al.; Horm. Metab. Res. 41, 221 (2009)
- Patients achieving clearance of HCV with interferon therapy recover from decreased retinol-binding protein 4 levels: M. Iwasa, et al.; J. Viral Hepat. 16, 716 (2009)
- Change in Serum Adipocytokines after Recovery of Thyroid Function and Weight in Patients with Graves' Disease: H.Y. Jung, et al.; Korean. J. Obes. 18, 47 (2009) [Korean]
- Macrophages are novel sites of expression and regulation of retinol binding protein-4 (RBP4): M. Broch, et al.; Physiol. Res. 59, 299 (2010)
- Combined Impact of Adiponectin and Retinol-binding Protein 4 on Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly People: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging: S. Lim, et al.; Obesity 18, 826 (2010)
- Elevated serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with insulin resistance in older women: J.B. Suh, et al.; Metabolism 59, 118 (2010)
- The APOA5?1131 T > C variant enhances the association between RBP4 and hypertriglyceridemia in diabetes: A. Cabré, et al.; Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 243 (2010)
- APOH is increased in the plasma and liver of type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome: A. Castro, et al.; Atherosclerosis 209, 201 (2010)
- Elevation of plasma retinol-binding protein 4 and reduction of plasma adiponectin in subjects with cerebral infarction: M. Sasaki, et al.; Metabolism 59, 527 (2010)
- Association of insulin resistance with anti-Mullerian hormone levels in women without polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): H.T. Park, et al.; Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 72, 26 (2010)
- Daily physical activity, fasting glucose, uric acid, and body mass index are independent factors associated with serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels: D. Cuevas-Ramos, et al.; Eur. J. Endocrinol. 163, 469 (2010)
- Adipokine pattern in subjects with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in comparison to normal glucose tolerance and diabetes: A. Tönjes, et al.; PLoS One. 5, e13911 (2010)
- Macrophages are novel sites of expression and regulation of retinol binding protein-4 (RBP4): M. Broch, et al.; Physiol. Res. 59, 299 (2010)
- Serum levels of placental growth factor and retinol-binding protein-4 in pregnancy-induced hypertensive women: A.F. Al-Kholy, et al.; J. Am. Sci. 6, 448 (2010)
- Elevated serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with insulin resistance in older women: J.B. Suh, et al.; Metabolism. 59, 118 (2010)
- The APOA5-1131 T>C variant enhances the association between RBP4 and hypertriglyceridemia in diabetes: A. Cabré, et al.; Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 243 (2010)
- Comparative analysis of serum proteomes of patients with cardiovascular disease: H.J. Kim, et al.; Clin. Biochem. 44, 178 (2011)
Relationship of serum retinol-binding protein 4 with weight status and lipid profile among Korean children and adults: I.K. Kim, et al.; Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 65, 226 (2011) - Identification of tuberculosis-associated proteins in whole blood supernatant: T. Tanaka, et al.; BMC Infect. Dis. 11, 71 (2011)
- Circulating Nampt and RBP4 levels in patients with carotid stenosis undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA): G. Aust, et al.; Clin. Chim. Acta. 412, 1195 (2011)
- High liver RBP4 protein content is associated with histological features in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C and with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: S. Petta, et al.; Dig. Liver Dis. 43, 404 (2011)
- Serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein, retinol-binding protein 4, and adiponectin concentrations in relation to the development of the metabolic syndrome in Korean boys: a 3-y prospective cohort study: K.M. Choi, et al.; Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 93, 19 (2011)
- Telmisartan reduces neointima volume and pulse wave velocity 8 months after zotarolimus-eluting stent implantation in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients: S.J. Hong, et al.; Heart 97, 1425 (2011)
- Retinol-binding protein 4 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in steatotic liver transplantation: A. Casillas-Ramírez, et al.; JPET 338, 143 (2011)
- Optimal cut points of waist circumference (WC) and visceral fat area (VFA) predicting for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in elderly population in the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA): S. Lim, et al.; Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 54, e29 (2012)
- Increased plasma levels of retinol-binding protein 4 with visceral obesity is associated with cardiovascular risk factors: J.C. Won, et al.; J. Diabet. Inv. 3, 457 (2012)
- Circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin, fetuin-a and retinol-binding protein in patients with tuberculosis: markers of metabolism and inflammation: N. Keicho, et al.; PLoS One 7, e38703 (2012)
- Endothelial impairment and bone marrow-derived CD34+/133+ cells in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction: M. Murata, et al.; J. Diab. Invest. 3, 526 (2012)
- Comparison of regional body composition and its relation with cardiometabolic risk between BMI-matched young and old subjects: Y. Lee, et al.; Atherosclerosis 224, 258 (2012)
- Association of subcutaneous and visceral fat mass with serum concentrations of adipokines in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: T. Saito, et al.; Endocr. J. 59, 39 (2012)
- Impact of Serum Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Levels on Regulation of Remnant-Like Particles Triglyceride in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: N. Yamaaki, et al.; J. Diabet. Res. 2013, ID143515 (2013)
- Crosstalk between circulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, adipokines and metabolic syndrome in obese subjects: K. Mirzaei, et al.; Diabetol. Metabol. Syndr. 5, 79 (2013)
- Associations of retinol-binding protein 4 with oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, and metabolic syndrome in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: Y. Liu, et al.; Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 6, 25 (2014)
- Adipokines may mediate the relationship between resting metabolic rates and bone mineral densities in obese women: S. Moradi, et al.; Osteoporos. Int. doi:10.1007/s00198-017-3914-6 (2017)
- Associations of dietary fats intake and adipokines levels in obese women: Y. Nasir, et al.; Clin. Nutr. ESPEN. 43, 390 (2021)