Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
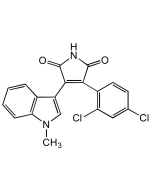
Ageladine A . trifluoracetate
As low as
260
CHF
CHF 260.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CMA-1001-C200200 µgCHF 260.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (4-(4,5-Dibromo-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]-pyridin-2-amine) . TFA |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C10H7Br2N5 . C2HF3O2 |
| MW | 357.0 . 114.0 |
| CAS | 950766-21-9 | 643020-13-7 (free base) |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from Agelas nakamurai. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | Brown solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or methanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Marnas Biochemicals. |
| Other Product Data |
Fluorescence specifications: |
| InChi Key | QAKGJAQGTQLMFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | NC1=NC2=C(N=CC=C2N1)C1=CC(Br)=C(Br)N1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Protect from light and moisture. Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. Stock solutions are stable for at least 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Non-toxic, pH-sensitive fluorescent dye (blue-green range) for live imaging of pH alteration in acidic organelles, vesicles, cells, tissue and even small whole animals over several days without side effects [2,4,5,7-9].
- Stronger fluorescent intensity under acidic conditions and barely detectable in alkaline solutions (wide range from pH 4 to pH 8) [2].
- Highly cell/membrane permeable. Trapped within the cells and acidic organelles through hydrophobic interactions with the inner side of the membranes [2].
- Barely metabolized and long-term stable, thus slow photobleaching [9].
- Angiogenesis inhibitor [1,3,6].
- Inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-1,-2,-8,-9,-12,-13 [1, 3-6].
- TYK2, DYRK2,Dyrk1A, YSK4 and RPS6KA1/2 inhibitor [3,5,6].
Product References
- Ageladine A: An antiangiogic matrixmetalloproteinase inhibitor from the marine sponge Agelas nakamurai: M. Fujita, et al.; JACS 125, 1570 (2003)
- Ageladine A, a pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid from marine sponges, is a pH sensitive membrane permeable dye: U. Bickmeyer, et al.; BBRC 373, 419 (2008)
- Synthesis and anticancer activities of ageladine A and structural analogs: Y. Ma, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 83 (2010)
- Tracking of fast moving neuronal vesicles with ageladine A: U. Bickmeyer, et al.; BBRC 402, 489 (2010)
- A one-pot synthesis and biological activity of ageladine A and analogues: S.R. Shengule, et al.; Med. Chem. 54, 2492 (2011)
- Synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase-12 inhibitory activity of ageladine A analogs: N. Ando & S. Terashima; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 59, 579 (2011)
- The alkaloid Ageladine A, originally isolated from marine sponges, used for pH-sensitive imaging of transparent marine animals: U. Bickmeyer; Mar. Drugs 10, 223 (2012)
- Incorporated nematocysts in Aeolidiella stephanieae (Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia, Aeolidoidea) mature by acidification shown by the pH sensitive fluorescing alkaloid Ageladine A: D. Obermann, et al.; Toxicon 60, 1108 (2012)
- Reporter dyes demonstrate functional expression of multidrug resistance proteins in the marine flatworm Macrostomum lignano: The sponge-derived dye ageladine A is not a substrate of these transporters: K. Tietje, et al.; Mar. Drugs 11, 3951 (2013)
- Marine-derived angiogenesis inhibitors for cancer therapy: Y.Q. Wang & Z.H. Miao; Mar. Drugs 11, 903 (2013)
- The physiological response of the marine platyhelminth Macrostomum lignano to different environmental oxygen concentrations: G.A. Rivera-Ingraham, et al.; J. Exp. Biol. 216, 2741 (2013)
- The chemically synthesized ageladine A-derivative LysoGlow84 stains lysosomes in viable mammalian brain cells and specific structures in the marine flatworm Macrostomum lignano: T. Mordhorst, et al.; Mar. Drugs 13, 920 (2015)