Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
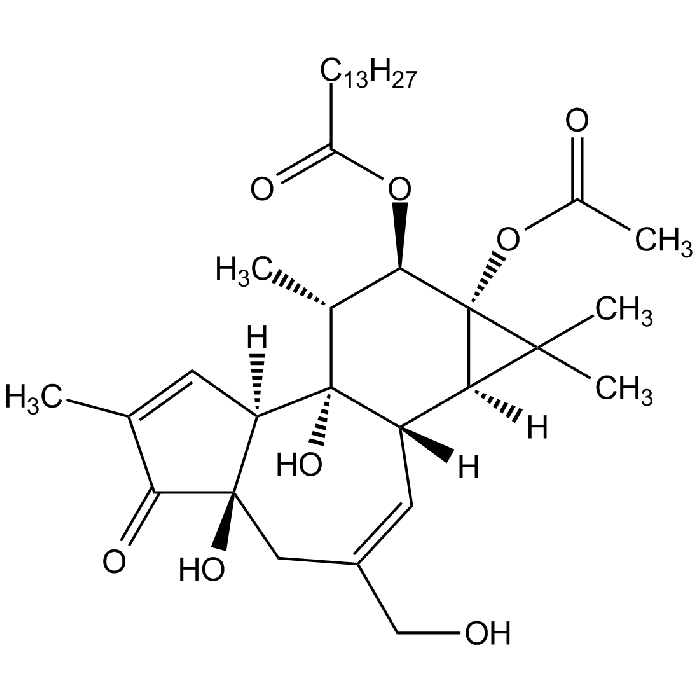
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate [PMA]
As low as
40
CHF
CHF 40.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0010-M0011 mgCHF 40.00
AG-CN2-0010-M0055 mgCHF 135.00
AG-CN2-0010-M01010 mgCHF 195.00
AG-CN2-0010-M02525 mgCHF 390.00
BULK available!
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PMA; TPA; 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C36H56O8 |
| MW | 616.8 |
| Merck Index | 14: 7332 |
| CAS | 16561-29-8 |
| RTECS | QH4377000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Semisynthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml), 100% ethanol (20mg/ml), methanol, acetone, ether or dimethylformamide; almost insoluble in aqueous buffers. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| Other Product Data |
Stock solutions are stable for up to 3 months at -20°C. |
| InChi Key | PHEDXBVPIONUQT-RGYGYFBISA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@]12[C@]3([H])C=C(CO)C[C@]4(O)C(=O)C(C)=C[C@@]4([H])[C@@]3(O)[C@H](C)[C@@H](OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@@]1(OC(C)=O)C2(C)C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- PMA/TPA is the most commonly-used phorbol ester.
- Binds to and activates protein kinase C (PKC) at nM concentrations.
- Induces cell growth arrest through a variety of pathways including the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways mediated by cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors such as p21WAF1/CIP1, p27KIP1, p15 and p16.
- Potent mouse skin tumor promoter.
- Promoter of inducible NOS (iNOS; NOS II).
- Apoptosis inducer.
- Potential effective cancer therapeutic agent.
- Inhibitor of anti-lipolytic activity of insulin.
- PMA treatment stimulates THP-1 cells and generates M0 macrophages (M0).
Product References
- In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 1: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 153 (1980)
- In vitro studies on the mode of action of the phorbol esters, potent tumor promoters: part 2: P.M. Blumberg; Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 8, 199 (1981)
- Skin tumor promotion by phorbol esters is a two-stage process: G. Fürstenberger, et al.; PNAS 78, 7722 (1981)
- Phorbol esters as signal transducers and tumor promoters: M. Castagna; Biol. Cell 59, 3 (1987), Review
- Phorbol esters induce nitric oxide synthase activity in rat hepatocytes. Antagonism with the induction elicited by lipopolysaccharide: S. Hortelano, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 267, 24937 (1992)
- Phorbol ester induces apoptosis in HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells but not in HL-60 PET mutant: D.E. Macfarlane & P.S. O'Donnel; Leukemia 7, 1846 (1993)
- Effect of intravenous infusions of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13- acetate (TPA) in patients with myelocytic leukemia: Preliminary studies on therapeutic efficacy and toxicity: T.H. Zheng, et al.; PNAS 95, 5357 (1998)
- 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced increase in depressed white blood cell counts in patients treated with cytotoxic cancer chemotherapeutic drugs: T.H. Zheng, et al.; PNAS 95, 5362 (1998)
- Characterization of phorbol esters activity on individual mammalian protein kinase C isoforms, using the yeast phenotypic assay: L. Saraiva, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 491, 101 (2004)
- Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate inhibits the antilipolytic action of insulin, probably via the activity of protein kinase Cε: J. Nakamura; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 648, 188 (2010)
- Characterization of polarized THP-1 macrophages and polarizing ability of LPS and food compounds: W. Chanput, et al.; Food Funct. 4, 266 (2013)
- M1 and M2 macrophages derived from THP-1 cells differentially modulate the response of cancer cells to etoposide: M. Genin, et al.; BMC Cancer 15, 577 (2015)
- The choice of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate differentiation protocol influences the response of THP-1 macrophages to a pro-inflammatory stimulus: M.E. Lund, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 430, 64 (2016)
- Vitamin D3 inhibits the proliferation of T helper cells, downregulate CD4+ T cell cytokines and upregulate inhibitory markers: V. Sheikh, et al. Human Immunol. 79, 439 (2018)
- Adults from Kisumu, Kenya have robust γδ T cell responses to Schistosoma mansoni, which are modulated by tuberculosis: T.A. McLaughlin, et al.; PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 14, e0008764 (2020)
- Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNγ+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes: E.W. Baxter, et al.; J. Immunol. Methods 478, 112721 (2020)
- Paeoniflorin reduces the inflammatory response of THP-1 cells by up‐regulating microRNA-124: D. Huang, et al.; Genes & Genomics 43, 623 (2021)
- Lymphatic dysfunction exacerbates cutaneous tumorigenesis and psoriasis-like skin inflammation through accumulation of inflammatory cytokines: H. Boki, et al.; J. Invest. Dermatol. 142, 1692 (2022)
- IL-17A and IFN-γ are Up-regulated in CD4 and γδ T Cells in Active Behcet's Disease Patients: V. Abbasova, et al.; Immunol. Lett. 242, 37 (2021)