Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
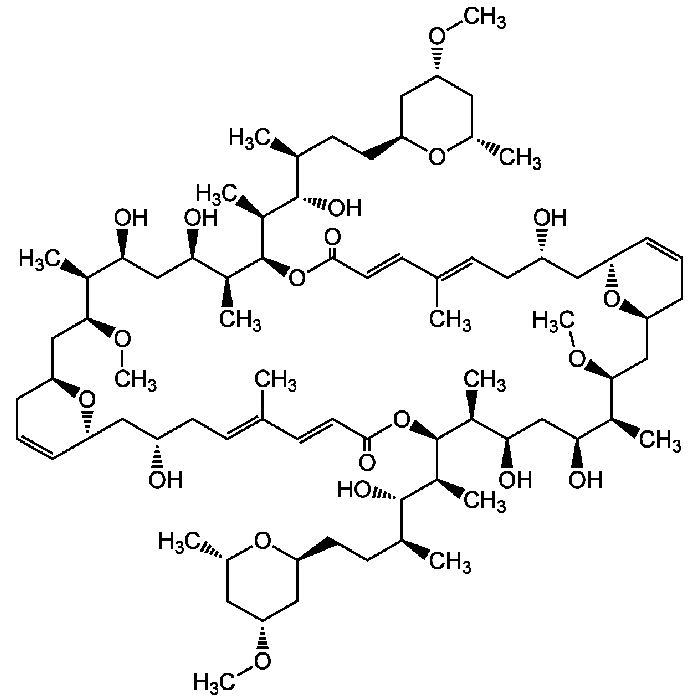
Swinholide A
As low as
120
CHF
CHF 120.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0035-C01010 µgCHF 120.00
AG-CN2-0035-C05050 µgCHF 350.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C78H132O20 |
| MW | 1389.9 |
| CAS | 95927-67-6 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colorless oil. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMSO, acetone or ethyl acetate. |
| InChi Key | RJVBVECTCMRNFG-VGHOFLFQSA-N |
| Smiles | CO[C@@H]1C[C@H](C)O[C@@H](CC[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@H]2OC(=O)\C=C\C(\C)=C\C[C@H](O)C[C@@H]3O[C@@H](CC=C3)C[C@H](OC)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@H](OC(=O)\C=C\C(\C)=C\C[C@H](O)C[C@H]3O[C@@H](CC=C3)C[C@H](OC)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2C)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)CC[C@H]2C[C@@H](C[C@H](C)O2)OC)C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable dimeric dilactone macrolide [1].
- Cytotoxic compound [1, 2, 7].
- Specific actin filament (F-actin) inhibitor. Disrupts the actin cytoskeleton by sequestering actin dimers and rapidly severing actin filaments (F-actin) [3, 5, 7, 8].
- Depolymerizes actin filaments (F-actin) [6].
- Antifungal [4].
- Apoptosis inducer [9].
- Alterates the actin cytoskeleton of GH4 cells and inhibits insulin-increased prolactin gene transcription [10].
Product References
- Marine natural products. XXIII. Three new cytotoxic dimeric macrolides, swinholides B and C and isoswinholide A, congeners of swinholide A, from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella swinhoei: M. Kobayashi, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 38, 2960 (1990)
- Marine natural products. XXXI. Structure-activity correlation of a potent cytotoxic dimeric macrolide swinholide A, from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella swinhoei, and its isomers: M. Kobayashi, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 42, 19 (1994)
- Swinholide A is a microfilament disrupting marine toxin that stabilizes actin dimers and severs actin filaments: M.R. Bubb, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 3463 (1995)
- Two classes of metabolites from Theonella swinhoei are localized in distinct populations of bacterial symbionts: C.A. Bewley, et al.; Experientia 52, 716 (1996)
- Use of the F-actin-binding drugs, misakinolide A and swinholide A: M.R. Bubb & I. Spector; Methods Enzymol. 298, 26 (1998)
- Actin-depolymerizing effect of dimeric macrolides, bistheonellide A and swinholide A: S.Y. Saito, et al.; J. Biochem. 123, 571 (1998)
- Actin-binding marine macrolides: total synthesis and biological importance: K.S. Yeung & I. Paterson; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 41, 4632 (2002) (Review)
- Structural basis of swinholide A binding to actin: V.A. Klenchin, et al.; Chem. Biol. 12, 287 (2005)
- Actin cytoskeleton derangement induces apoptosis in renal ischemia/reperfusion: M. Genescà, et al.; Apoptosis 11, 563 (2006)
- Insulin-increased prolactin gene expression requires actin treadmilling: potential role for p21 activated kinase: F.M. Stanley; Endocrinol. 148, 5874 (2007)
- Pointed-end processive elongation of actin filaments by Vibrio effectors VopF and VopL: E. Kudryashova, et al.; Sci. Adv. 8, eadc9239 (2022)