Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Jasplakinolide (high purity)
As low as
260
CHF
CHF 260.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0037-C05050 µgCHF 260.00
AG-CN2-0037-C100100 µgCHF 420.00
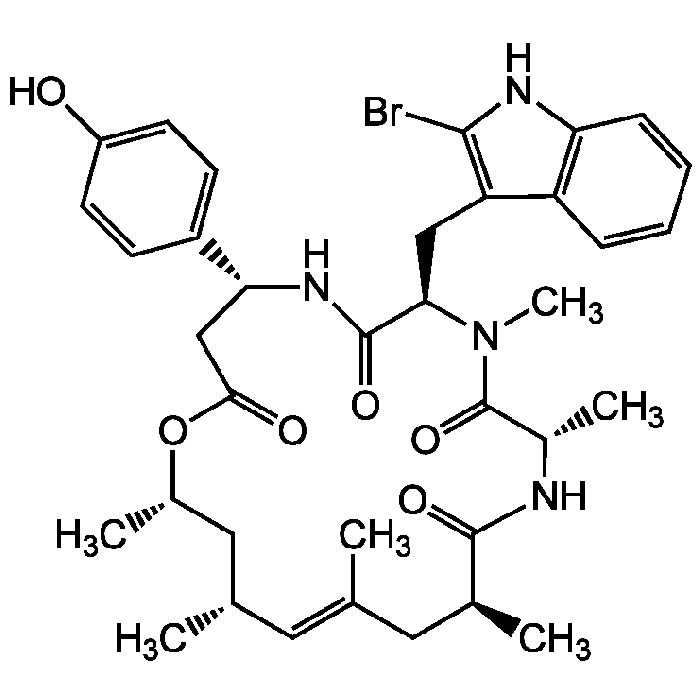
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Jaspamide; NSC 613009 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C36H45BrN4O6 |
| MW | 709.7 |
| CAS | 102396-24-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Jaspis splendens. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by MS. |
| InChi Key | GQWYWHOHRVVHAP-DHKPLNAMSA-N |
| Smiles | C[C@H]1C[C@@H](C)\C=C(C)\C[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N(C)[C@H](CC2=C(Br)NC3=C2C=CC=C3)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(=O)O1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable, non-fluorescent F-actin probe [3, 8, 12].
- Potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization [3, 8, 12].
- Competes with phallotoxins for actin binding [3].
- Antifungal and antiparasitic compound [1, 2, 9].
- Antiproliferative and anticancer compound [3, 4, 5].
- Apoptosis enhancer/inducer [6, 10].
- Tool used for autophagy/phagocytosis research [7, 11, 13].
Product References
- Jasplakinolide, a cyclodepsipeptide from the marine sponge, Jaspis sp: P. Crews, et al.; Tetrahedron Lett. 27, 2797 (1986)
- Jaspamide, a modified peptide from a Jaspis sponge, with insecticidal and antifungal activity: T.M. Zabriskie, et al.; JACS 108, 3123 (1986)
- Jasplakinolide, a cytotoxic natural product, induces actin polymerization and competitively inhibits the binding of phalloidin to F-actin: M.R. Bubb, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14869 (1994)
- Jasplakinolide's inhibition of the growth of prostate carcinoma cells in vitro with disruption of the actin cytoskeleton: A.M. Senderowicz, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87, 46 (1995)
- Growth modulation and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells by jaspamide: I. Fabian, et al.; Exp. Hematol. 23, 583 (1995)
- Actin stabilization by jasplakinolide enhances apoptosis induced by cytokine deprivation: S.C. Posey & B.E. Bierer; J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4259 (1999)
- Alteration of actin organization by jaspamide inhibits ruffling, but not phagocytosis or oxidative burst, in HL-60 cells and human monocytes: I. Fabian, et al.; Blood 93, 3994 (1999)
- Jasplakinolide. An actin-specific reagent that promotes actin polymerization: A. Holzinger; Methods Mol. Biol. 161, 109 (2001) (Review)
- Effect of jasplakinolide on the growth, invasion, and actin cytoskeleton of Plasmodium falciparum: Y. Mizuno, et al.; Parasitol. Res. 88, 844 (2002)
- Induction of apoptosis and CD10/neutral endopeptidase expression by jaspamide in HL-60 line cells: D.P. Cioca & K. Kitano; Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59, 1377 (2002)
- Clearance of a Hirano body-like F-actin aggresome generated by jasplakinolide: F. Lázaro-Diéguez, et al.; Autophagy 4, 717 (2008)
- Jasplakinolide: an actin-specific reagent that promotes actin polymerization: A. Holzinger; Methods Mol. Biol. 586, 71 (2009) (Review)
- Dynamic macrophage "probing" is required for the efficient capture of phagocytic targets: R.S. Flannagan, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 191, 1205 (2010)