Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
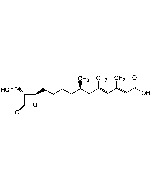
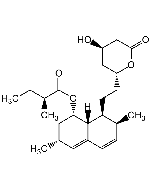
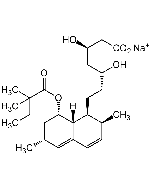
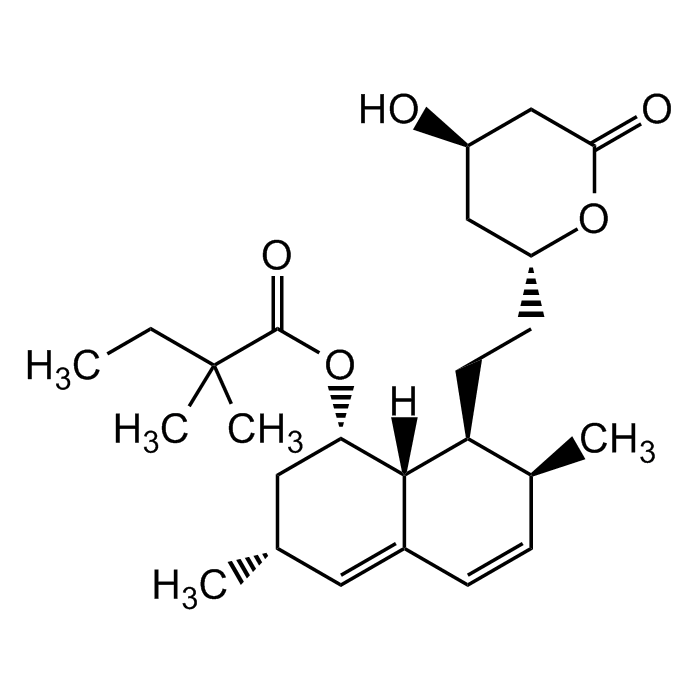
Simvastatin
As low as
28
CHF
CHF 28.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0052-M01010 mgCHF 28.00
AG-CN2-0052-M05050 mgCHF 45.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MK-733; Synvinolin; BRN 4768037 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C25H38O5 |
| MW | 418.6 |
| Merck Index | 14: 8539 |
| CAS | 79902-63-9 |
| RTECS | EK7798000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or methanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by UV and IR. |
| InChi Key | RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@]12[C@H](C[C@@H](C)C=C1C=C[C@H](C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1)OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Synthetic analog of Lovastatin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0051).
- Potent competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
- Anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Cholesterol/isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitor. Blocks the production of mevalonate, a critical compound in the production of cholesterol and isoprenoids.
- Inhibits the isoprenylation of Ras and Rho family GTPases .
- Anticancer compound that causes cell cycle arrest in G1 and G2/M phases through modulation of proteasome in cancer cell lines.
- SKP2 E3 ligase inhibitor. Decreases the expression of Skp2 and results in the inhibition of Skp2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p27 and p21, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
- Smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor.
- Anti-adhesive, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compound that stimulates bone formation. Suppresses TNF-induced NF-κB activation.
- Increases cellular resistance to anticancer agents such as doxorubicin and etoposides (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3572).
- Suppresses ICAM-1-LFA-1 interactions, which blocks virus replication and infection.
- Anti-hypertensive agent.
- Inhibitor of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation by promoting ferroptosis.
Product References
- Effects of synvinolin (MK-733) on plasma lipids in familial hypercholesterolaemia: M.J. Mol, et al.; Lancet 2, 936 (1986)
- All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated: J.F. Hancock, et al.; Cell 57, 1167 (1989)
- Inhibition of proliferation of human smooth muscle cells by various HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors; comparison with other human cell types: P. Negre-Aminou, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1345, 259 (1997)
- Statins as a newly recognized type of immunomodulator: B. Kwak, et al.; Nat. Med. 6, 1399 (2000)
- Lovastatin and simvastatin are modulators of the proteasome: C. Wojcik, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32, 957 (2000)
- Statins and bone formation: I.R. Garrett, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 7, 715 (2001)
- HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors as immunomodulators: potential use in transplant rejection: L.J. Raggatt & N.C. Partridge; Drugs 62, 2185 (2002) (Review)
- HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and the malignant cell: the statin family of drugs as triggers of tumor-specific apoptosis: W.W. Wong, et al.; Leukemia 16, 508 (2002)
- The statins as anticancer agents: K.K. Chan, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 9,10 (2003)
- Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of statins: L.M. Blanco-Colio, et al.; Kidney Int. 63, 12 (2003)
- Statin compounds reduce human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by preventing the interaction between virion-associated host intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and its natural cell surface ligand LFA-1: J.F. Giguere & M.J. Tremblay; J. Virol. 78, 12062 (2004)
- HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) to treat Epstein-Barr virus-driven lymphoma: J.I. Cohen; Br. J. Canc. 92, 1593 (2005)
- Beyond lipid lowering: the anti-hypertensive role of statins: V. Chopra, et al.; Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 21, 161 (2007)
- Reversal of chemoresistance and enhancement of apoptosis by statins through down-regulation of the NF-κB pathway: K.S. Ahn, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 75, 907 (2008)
- Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21 accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: S.-T. Wang, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 8, e2626 (2017)
- Simvastatin inhibits hepatic stellate cells activation by regulating the ferroptosis signaling pathway: K. Kitsugi, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 166750 ahead of print (2023)