Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
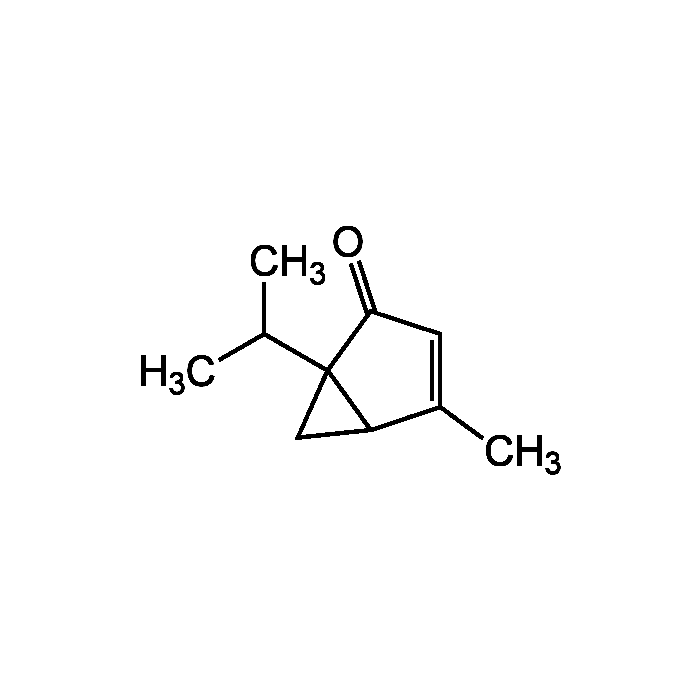
Umbellulone
As low as
180
CHF
CHF 180.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0085-M01010 mgCHF 180.00
AG-CN2-0085-M100100 mgCHF 1’260.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (-)-Umbellulone; Umbellol; NSC 22046; BRN 2042730; Oreodaphnol; 3-Thujen-2-one |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C10H14O |
| MW | 150.2 |
| CAS | 546-78-1 |
| RTECS | XP0200000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Umbellularia californica Nutt. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colourless oil. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or ethanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Density: 1.057 ± 0.06g/cm3(mL) Irritant: Umbellulone is a headache-inducing monoterpene ketone. Can induce headache when inhaling. Caution should be taken when dealing with this substance. |
| InChi Key | LTTVJAQLCIHAFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC(C)C12CC1C(C)=CC2=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Offensive principle of the so-called "headache tree".
- Causes a painful cold sensation.
- Selective TRPA1 activator. Weak TRPM8 activator.
- Releases CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) after TRPA1 activation which leads to activation of trigeminovascular pathways and CGRP-mediated neurogenic vasodilatation relevant to produce headache/migraine.
Product References
- Umbellulone modulates TRP channels: J. Zhong, et al.; Pflugers Arch. 462, 861 (2011)
- The 'headache tree' via umbellulone and TRPA1 activates the trigeminovascular system: R. Nassini, et al.; Brain 135, 376 (2012)
- Activation of TRPA1 on dural afferents: a potential mechanism of headache pain: R.M. Edelmayer, et al.; Pain 153, 1949 (2012)