Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
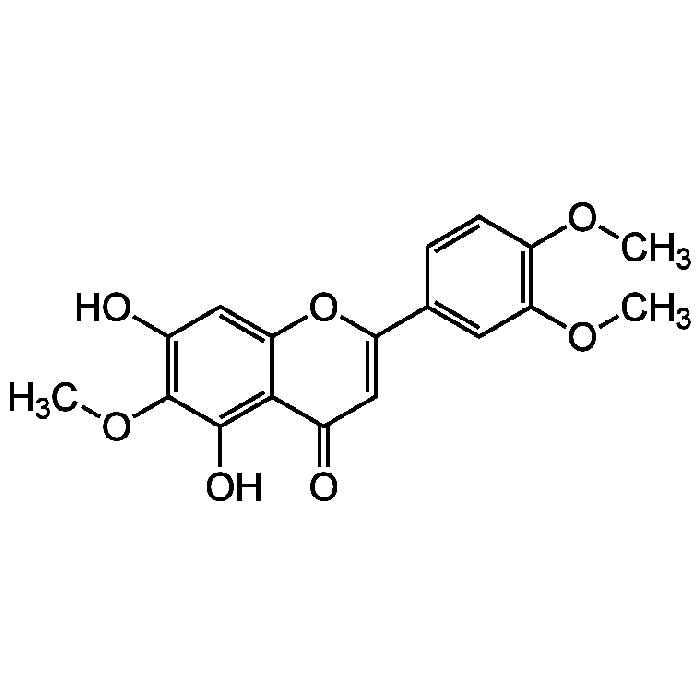
Eupatilin
As low as
70
CHF
CHF 70.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0432-M0055 mgCHF 70.00
AG-CN2-0432-M02525 mgCHF 280.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone; NSC 122413 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C18H16O7 |
| MW | 344.3 |
| CAS | 22368-21-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Artemisia sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Pale yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, hot methanol or mixture of methanol and chloroform. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | DRRWBCNQOKKKOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)O)OC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. Protect from moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase.
- Anti-proliferative and anticancer compound.
- Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest inducer.
- Inhibits ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-κB activation and expression of Raf-1 and Ras.
- PI3K Class I, MKK3/6 and MKK4 inhibitor.
- Inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression.
- Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent.
- Antioxidant.
- Antidiabetic. Enhances hepatic and plasma glucose metabolism and increases insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic mice.
- Selective PPARα agonist.
- Neuroprotective.
Product References
- Selective inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by natural compounds isolated from Chinese plants, Artemisia rubripes Nakai: Y. Koshihara, et al.; FEBS Lett. 158, 41 (1983)
- Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells: H.J. Seo & Y.J. Surh; Mutat. Res. 496, 191-8 (2001)
- Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces cell cycle arrest in ras-transformed human mammary epithelial cells: D.H. Kim, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 68, 1081 (2004)
- Eupatilin blocks mediator release via tyrosine kinase inhibition in activated guinea pig lung mast cells: J.Y Kim, et al.; J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A. 68, 2063 (2005)
- Eupatilin has an antiapoptotic action on hepatocytes, in contrast to apoptotic actions on other cells: T. Mine; J. Gastroenterol. 41, 818 (2006)
- Eupatilin protects gastric epithelial cells from oxidative damage and down-regulates genes responsible for the cellular oxidative stress: E.J. Choi, et al.; Pharm. Res. 25, 1355 (2008)
- Eupatilin inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced apoptotic cell death through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB: S. Lee, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 2865 (2008)
- Eupatilin, isolated from Artemisia princeps Pampanini, enhances hepatic glucose metabolism and pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice: Y.J. Kang, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 82, 25 (2008)
- Eupatilin exhibits a novel anti-tumor activity through the induction of cell cycle arrest and differentiation of gastric carcinoma AGS cells: E.J. Choi, et al.; Differentiation 77, 412 (2009)
- Eupatilin inhibits T-cell activation by modulation of intracellular calcium flux and NF-kappaB and NF-AT activity: Y.D. Kim, et al.; J. Cell Biochem. 108, 225 (2009)
- Eupatilin Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cell Growth by Blocking STAT3-Mediated VEGF Expression: J.H. Cheong, et al.; J. Gastric Cancer 11, 16 (2011)
- The neuroprotective effect of eupatilin against ischemia/reperfusion-induced delayed neuronal damage in mice: M. Cai, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 689, 104 (2012)
- Eupatilin, a major flavonoid of Artemisia, attenuates aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting PI3K, MKK3/6, and MKK4 activities: J.E. Son, et al.; Planta Med. 79, 1009 (2013)
- Massive elimination of multinucleated osteoclasts by eupatilin is due to dual inhibition of transcription and cytoskeletal rearrangement: J.-Y. Kim, et al.; Bone Rep. 3, 83 (2015)
- Identification of eupatilin from Artemisia argyi as a selective PPARα agonist using affinity selection ultrafiltration LC-MS: Y. Choi, et al.; Molecules 20, 13753 (2015)
- Eupatilin suppresses the allergic inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo: E-H. Song, et al.; Phytomed. 42, 1 (2018)