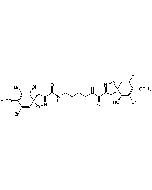Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
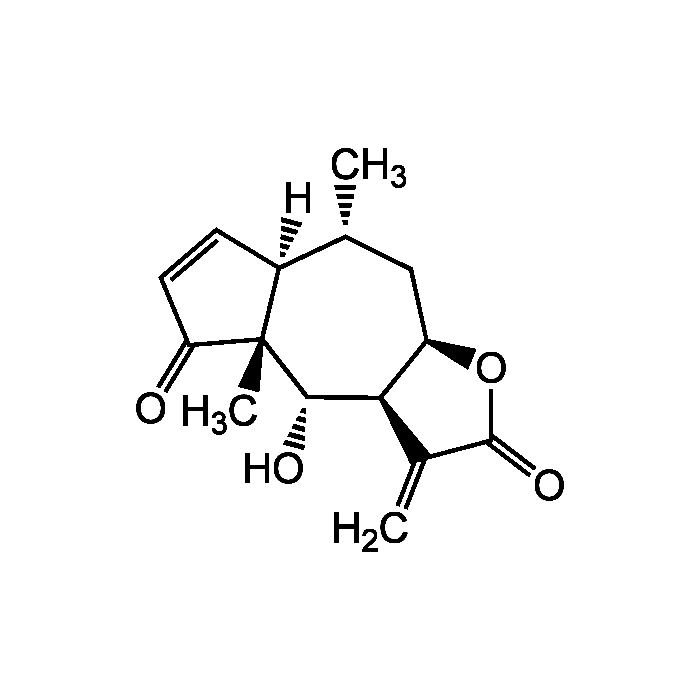
Helenalin
As low as
280
CHF
CHF 280.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0435-C500500 µgCHF 280.00
AG-CN2-0435-M0011 mgCHF 480.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Helenalin A; NSC 85236 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H18O4 |
| MW | 262.3 |
| CAS | 6754-13-8 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Arnica montana. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥96% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | ZVLOPMNVFLSSAA-XEPQRQSNSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12C=CC(=O)[C@@]1(C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1[C@@H](C[C@H]2C)OC(=O)C1=C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Anticancer compound.
- NF-κB inhibitor.
- Apoptosis inducer.
- Potent anti-inflammatory agent.
- Telomerase inhibitor.
- Anti-trypanosomal and antiprotozoal compound
- Antibiotic.
- Shows anti-proliferative effects in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.
- Autophagy inducer.
Product References
- Constituents of Helenium species.XIII. The structure of Helenalin and Mexicanin A: W. Herz, et al.; JACS 85, 19 (1963)
- Antitumor agents. 21. A proposed mechanism for inhibition of cancer growth by tenulin and helenalin and related cyclopentenones: I.H. Hall, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 20, 333 (1977)
- Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis in P-388 lymphocytic leukemia tumor cells by helenalin and bis(helenalinyl)malonate in vivo: W.L. Williams Jr, et al.; J. Pharm. Sci. 77, 178 (1988)
- Helenalin, an anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone from Arnica, selectively inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB: G. Lyss, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 378, 951 (1997)
- The anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone helenalin inhibits the transcription factor NF-kappaB by directly targeting p65: G. Lyss, et al; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33508 (1998)
- Helenalin triggers a CD95 death receptor-independent apoptosis that is not affected by overexpression of Bcl-x(L) or Bcl-2: V.M. Dirsch, et al.; Cancer Res. 61, 5817 (2001)
- Anti-trypanosomal activity of helenalin and some structurally related sesquiterpene lactones: T.J. Schmidt, et al.; Planta Med. 68, 750 (2002)
- Induction of human leukemia HL-60 cell differentiation via a PKC/ERK pathway by helenalin, a pseudoguainolide sesquiterpene lactone: S.H. Kim, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 511, 89 (2005)
- Potent inhibition of human telomerase by helenalin: P.R. Huang, et al.; Cancer Lett. 227, 169 (2005)
- Novel effect of helenalin on Akt signaling and Skp2 expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: C.A. Auld, et al.; BBRC 346, 314 (2006)
- Helenalin reduces Staphylococcus aureus infection in vitro and in vivo: D. Boulanger, et al.; Vet. Microbiol. 119, 330 (2007)
- Helenalin-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of p21(Cip1) inhibits 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation: K.M. Fernandes, et al.; J. Cell Biochem. 105, 913 (2008)
- Helenalin suppresses essential immune functions of activated CD4+ T cells by multiple mechanisms: C. Berges, et al.; Mol. Immunol. 46, 2892 (2009)
- Helenalin bypasses Bcl-2-mediated cell death resistance by inhibiting NF-κB and promoting reactive oxygen species generation: R. Hoffmann, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 82, 453 (2011)
- NF-κB p65 repression by the sesquiterpene lactone, Helenalin, contributes to the induction of autophagy cell death: C.B. Lim, et al.; BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 12, 93 (2012)
- Natural sesquiterpene lactones induce programmed cell death in Trypanosoma cruzi: a new therapeutic target?: V. Jimenez, et al.; Phytomedicine 21, 1411 (2014)