Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
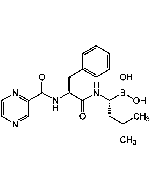
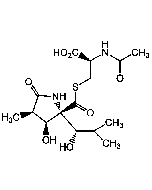
Salinosporamide A
As low as
CHF 0.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0444-C100100 µgCHF 160.00
AG-CN2-0444-M0011 mgCHF 720.00
AG-CN2-0444-M0055 mgCHF 2’500.00
AG-CN2-0444-M05050 mgINQ
BULK available!
Research Use Only (RUO). NOT ALLOWED FOR USE IN HUMANS.

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SalA; Marizomib; NPI-0052 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H20ClNO4 |
| MW | 313.8 |
| CAS | 437742-34-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Salinospora tropica. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. Do not dissolve in methanol or ethanol. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Note: We recommend to use fresh solutions. Aliquots should be prepared in DMSO and stored at -20°C. |
| InChi Key | NGWSFRIPKNWYAO-SHTIJGAHSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@](O)([C@@]1([H])CCCC=C1)[C@@]12NC(=O)[C@H](CCCl)[C@]1(C)OC2=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep under inert gas. Protect from light. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Potent, irreversible inhibitor of all the 3 proteolytic activities of the mammalian 20S proteasome.
- β5 subunit: chymotrypsin-like (EC50 = 3.5nM)
- β2 subunit: trypsin-like (EC50 = 28nM)
- β1 subunit: caspase-like or peptidyl-glutamyl peptide-hydrolyzing (PGPH) (EC50 = 430nM)
- Potent anticancer compound.
- Triggers apoptosis, with distinct proteasome activity and mechanism of action compared to bortezomib (Velcade) (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3602).
- Most potent suppressor of NF-κB activation, compared with bortezomib, MG-132 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-0011), N-acetyl-leucyl-leucyl-norleucinal (ALLN) and lactacystin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0104).
- Inhibitor of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, ICAM-1 and VEGF synthesis.
- Displays a longer inhibition duration than bortezomib.
- Potent antileukemic activity against bortezomib-resistant leukemia cells.
Product References
- Salinosporamide A: a highly cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from a novel microbial source, a marine bacterium of the new genus salinospora: R.H. Feling, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 355 (2003)
- Structure-activity relationship studies of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052), a novel marine derived proteasome inhibitor: V.R. Macherla, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 48, 3684 (2005)
- A novel orally active proteasome inhibitor induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells with mechanisms distinct from Bortezomib: D. Chauhan, et al.; Cancer Cell 8, 407 (2005)
- Crystal structures of Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) and B (NPI-0047) in complex with the 20S proteasome reveal important consequences of beta-lactone ring opening and a mechanism for irreversible binding: M. Groll, et al.; JACS 128, 5136 (2006)
- NPI-0052 enhances tumoricidal response to conventional cancer therapy in a colon cancer model: J.C. Cusack, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 6758 (2006)
- Comparison of biochemical and biological effects of ML858 (salinosporamide A) and bortezomib: M.J. Williamson, et al.; Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 3052 (2006)
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through down-modulation of NF-κB-regulated gene products: K.S. Ahn, et al.; Blood 110, 2286 (2007)
- A mechanistic and kinetic study of the beta-lactone hydrolysis of Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052), a novel proteasome inhibitor: N. Denora, et al.; J. Pharm. Sci. 96, 2037 (2007)
- Combination of proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and NPI-0052 trigger in vivo synergistic cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma: D. Chauhan, et al.; Blood 111, 1654 (2008)
- Discovery and development of the anticancer agent salinosporamide A (NPI-0052): W. Fenical, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17, 2175 (2009)
- Generating a generation of proteasome inhibitors: from microbial fermentation to total synthesis of salinosporamide a (marizomib) and other salinosporamides: B.C. Potts & K.S. Lam; Mar. Drugs 8, 835 (2010) (Review)
- Salinosporamide natural products: Potent 20S proteasome inhibitors as promising cancer chemotherapeutics: T.A. Gulder & B.S. Moore; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49, 9346 (2010) (Review)
- Marizomib, a proteasome inhibitor for all seasons: preclinical profile and a framework for clinical trials: B.C. Potts, et al.; Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 11, 254 (2011)
- Proteasome regulator marizomib (NPI-0052) exhibits prolonged inhibition, attenuated efflux, and greater cytotoxicity than its reversible analogs: A. Obaidat, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 337, 479 (2011)
- Molecular mechanisms of acquired proteasome inhibitor resistance: A.J. Kale & B.S. Moore; J. Med. Chem. 55, 10317 (2012)
- Antileukemic activity and mechanism of drug resistance to the marine Salinispora tropica proteasome inhibitor salinosporamide A (Marizomib): D. Niewerth, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 86, 12 (2014)
- NPI-0052 and γ-radiation induce a synergistic apoptotic effect in medulloblastoma: E. Frisira, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 10, 785 (2019)
- Proteasome Inhibition in Multiple Myeloma: Head-to-Head Comparison of Currently Available Proteasome Inhibitors: A. Besse, et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. 26, 340 (2019)