Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
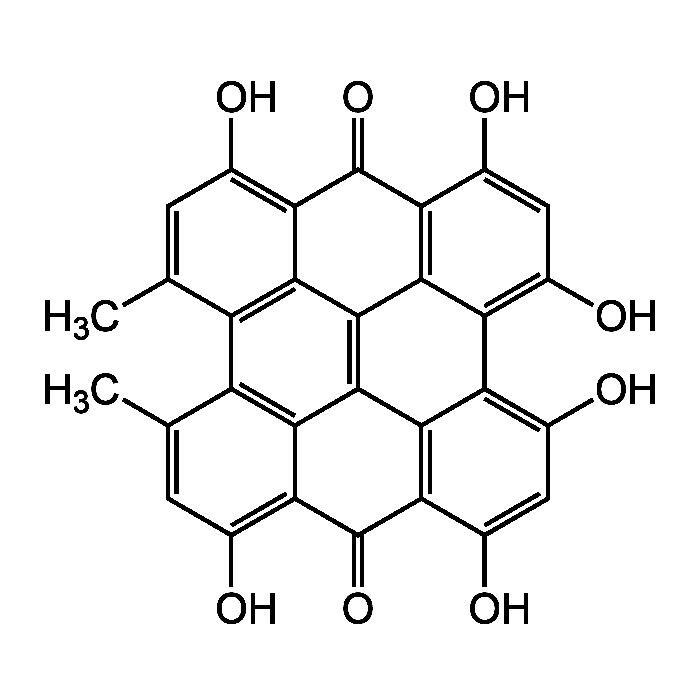
Hypericin
As low as
65
CHF
CHF 65.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0449-M0011 mgCHF 65.00
AG-CN2-0449-M0055 mgCHF 250.00
AG-CN2-0449-M01010 mgCHF 320.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Mycoporphyrin; NSC407313; Hypericum red |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C30H16O8 |
| MW | 504.5 |
| Merck Index | 14: 4863 |
| CAS | 548-04-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Hypericum perforatum. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Dark brown to black-red solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in 100% ethanol, methanol or DMSO. In pure water, hypericin forms aggregates which are non-soluble and non-fluorescent. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| InChi Key | BTXNYTINYBABQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC1=CC(O)=C2C(=O)C3=C4C(=C(O)C=C3O)C3=C(O)C=C(O)C5=C3C3=C4C2=C1C1=C3C(=C(O)C=C1C)C5=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Keep under inert gas. Protect from light. Protect from moisture and oxygen. Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- One of the principal active constituents of St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum).
- Hypericin is a photosensitive pigment/chromophore with bright red fluorescence emission (λmax: 594nm).
- Has a high triplet quantum yield and ability to produce considerable amounts of singlet oxygen and other ROS species when photoactivated.
- Antiviral, anticancer and antidepressant agent.
- Inactivates enveloped viruses (including HIV).
- This photosensitizing agent has shown to induce apoptosis and necrosis in cancer cells during photodynamic therapy.
- Selective inhibitor of protein kinase C (PKC). Has been shown to inhibit other kinases and targets such as EGFR-PTK, PI3K, CKII, MAPK and insulin receptor (IR).
- Necrosis-avid contrast agent investigated for use in non-invasively targeting necrotic tissues, based on to be defined components in the phospholipid bilayer.
Product References
- On the absorption spectrum of hypericin: N. Pace & G. Mackinney; JACS 61, 3594 (1939)
- Hypericin and its photodynamic action: N. Duran & P.S. Song; Photochem. Photobiol. 43, 677 (1986) (Review)
- Hypericin and pseudohypericin specifically inhibit protein kinase C: possible relation to their antiretroviral activity: I. Takahashi, et al.; BBRC 165, 1207 (1989)
- Virucidal Activity of Hypericin Against Enveloped and Non-enveloped DNA and RNA Viruses: J. Tang, et al.; Antivir. Res. 13, 313 (1990)
- Agents for treating human immunodeficiency virus infection: E.P. Acosta & C.V. Fletcher; Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 51, 2251 (1994) (Review)
- Photosensitized inhibition of growth factor-regulated protein kinases by hypericin: P. Agostinis, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 49, 1615 (1995)
- The chemical and biological properties of hypericin - a compound with a broad spectrum of biological activities: G. Lavie, et al.; Med. Res. Rev. 15, 111 (1995) (Review)
- Natural products derived from plants as potential drugs for the photodynamic destruction of tumor cells: R. Ebermann, et al.; J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 36, 95 (1996) (Review)
- Apoptotic and anti-apoptotic signaling pathways induced by photodynamic therapy with hypericin: P. Agostinis, et al.; Adv. Enzyme Regul. 40, 157 (2000) (Review)
- St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.): a review of its chemistry, pharmacology and clinical properties: J. Barnes, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 53, 583 (2001) (Review)
- Hypericin in cancer treatment: more light on the way: P. Agostinis, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34, 221 (2002) (Review)
- Hypericin - a new antiviral and antitumor photosensitizer: mechanism of action and interaction with biological macromolecules: P. Miskovsky; Curr. Drug Targets 3, 55 (2002) (Review)
- Mechanism of action of St John's wort in depression: what is known? V. Butterweck; CNS Drugs 17, 539 (2003) (Review)
- Cell death and growth arrest in response to photodynamic therapy with membrane-bound photosensitizers: J. Piette, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 66, 1651 (2003) (Review)
- Hypericin - the facts about a controversial agent: A. Kubin, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 11, 233 (2005)
- The multifaceted photocytotoxic profile of hypericin: T.A. Theodossiou, et al.; Mol. Pharm. 6, 1775 (2009) (Review)
- Molecular response to hypericin-induced photodamage: B. Krammer & T. Verwanger; Curr. Med. Chem. 19, 793 (2012) (Review)
- Necrosis avidity: a newly discovered feature of hypericin and its preclinical applications in necrosis imaging: B. Jiang, et al.; Theranostics 3, 667 (2013) (Review)
- Hypericin in the light and in the dark: Two sides of the same coin: Z. Jendzelovska, et al.; Front. Plant Sci. 7, 560 (2016) (Review)






