Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
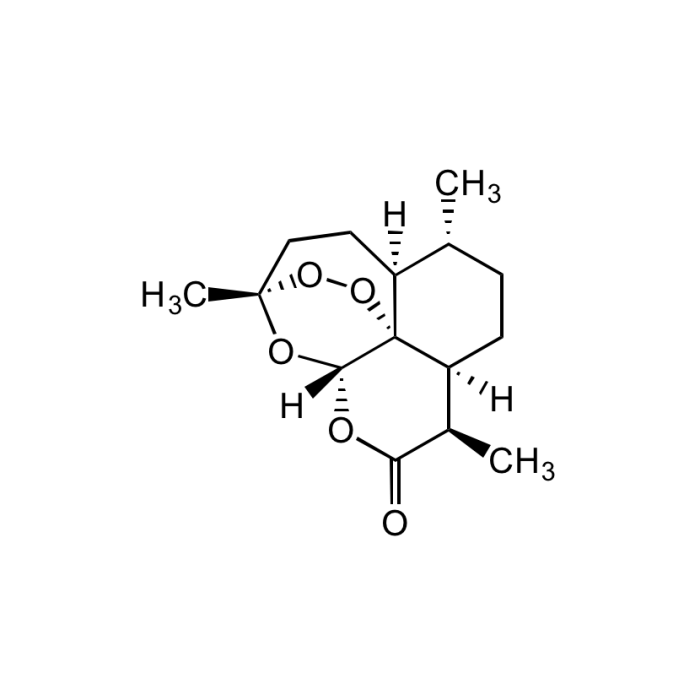
Artemisinin
As low as
55
CHF
CHF 55.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0467-M100100 mgCHF 55.00
AG-CN2-0467-M500500 mgCHF 130.00
AG-CN2-0467-G0011 gCHF 250.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Qinghaosu; Arteannuin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H22O5 |
| MW | 282.3 |
| CAS | 63968-64-9 |
| RTECS | KD4170000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Artemisia annua. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or ethanol. |
| InChi Key | BLUAFEHZUWYNDE-NNWCWBAJSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12CC[C@@H](C)[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4(C)OO[C@@]13[C@]([H])(OC(=O)[C@@H]2C)O4 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Anti-malaria.
- Apoptosis inducer.
- Anti-cancer.
- Inhibits production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and nitric oxide (NO).
- Functional ARX inhibitor. Enhancer of GABAA signaling. Shown to promote the in vivo conversion of pancreatic α cells into functional β-like cells through enhanced GABA signaling and may have potential as a therapeutic for diabetes.
- Targets Gephyrin.
Product References
- Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China: D.L. Klayman; Science 228, 1049 (1985)
- The development of the antimalarial drugs with new type of chemical structure--qinghaosu and dihydroqinghaosu: Y. Tu; SE Asian J. Trop. Med. Publ. Health 35, 250 (2004)
- Artemisinin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells: N.P. Singh & H.C. Lai; Anticancer Res. 24, 2277 (2004)
- Artemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-κB pathway in microglia cells: C. Zhu, et al.; PLoS One 7, e35125 (2012)
- Differential effect of artemisinin against cancer cell lines: M. Tilaoui, et al.; Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 4, 189 (2014)
- Artemisinins target GABAA receptor signaling and impair α cell identity: J. Li, et al.; Cell 168, 86 (2017)