Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
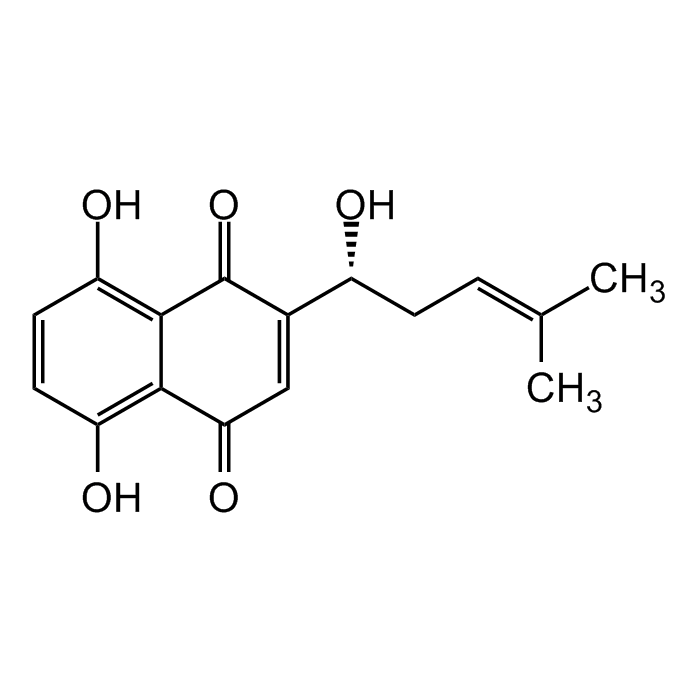
Shikonin
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0487-M01010 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CN2-0487-M05050 mgCHF 200.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (+)-Shikonin; (R)-Shikonin; Tokyo Violet; NSC 252844; Isoarnebin 4; C.I. 75535; (R)-5,8-Dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-4-methylpent-3-en-1-yl)naphthalene-1,4-dione |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C16H16O5 |
| MW | 288.3 |
| CAS | 517-89-5 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Alkanna sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Purple red solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or DMF. Sparingly soluble in ethanol, methanol or water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | NEZONWMXZKDMKF-SNVBAGLBSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=C2C(C(C=C([C@H](O)C/C=C(C)/C)C2=O)=O)=C(O)C=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Anticancer compound. Inhibits TNF-α-induced and B-16 melanoma-induced angiogenesis.
- Induces apoptosis and RIP1- and RIP3-dependent necroptosis in several cancer cells. Circumvents cancer antidrug resistance through the necroptosis pathway.
- Proteasome inhibitor. Autophagy inducer.
- Topoisomerase I inhibitor.
- Inhibits glycolysis in cancer cells by inhibiting tumor-specific pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2).
- Anti-inflammatory compound. Inhibits leukocyte migration, downregulates chemokine receptor expression, and inhibits HIV-1 replication.
- Inhibits the activation of NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome. Shown to directly target caspase-1 and as a inhibitor of PKM2 to block PKM2-mediated glycolysis that promotes inflammasome activation by modulating EIF2AK2 phosphorylation in macrophages.
- Antioxidant. Free radical scavenger.
- Directly inhibits nitric oxide synthase (NOS).
- Regulator of systemic glucose tolerance, energy balance and adiposity/obesity. Adipogenesis inhibitor. Shown to inhibit fat accumulation in adipocytes.
- Antibacterial and antifungal agent.
- Shown to potentially inhibit the 33.8-kDa Main Protease (Mpro)/3C-like Protease of SARS-CoV-2, consequently inhibiting viral transcription and replication and possibly inhibiting spread of COVID-19.
Product References
- Antitumor activity of shikonin and its derivatives: U. Sankawa, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 25, 2392 (1977)
- A comparative study on anti-inflammatory activities of the enantiomers, shikonin and alkannin: S. Tanaka, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 49, 466 (1986)
- Shikonin, an ingredient of Lithospermum erythrorhizon, inhibits angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro: T. Hisa, et al.; Anticancer Res. 18, 783 (1998)
- Shikonin, a component of antiinflammatory Chinese herbal medicine, selectively blocks chemokine binding to CC chemokine receptor-1: X. Chen, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 1, 229 (2001)
- Shikonin, a component of chinese herbal medicine, inhibits chemokine receptor function and suppresses human immunodeficiency virus type 1: X. Chen, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 2810 (2003)
- Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells: X. Mao, et al.; Cell Res. 18, 879 (2008)
- Dual role of shikonin in early and late stages of collagen type II arthritis: Q. Dai, et al.; Mol. Biol. Rep. 36, 1597 (2009)
- Shikonin exerts antitumor activity via proteasome inhibition and cell death induction in vitro and in vivo: H. Yang, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 124, 2450 (2009)
- Shikonin inhibits fat accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: H. Lee, et al.; Phytother. Res. 24, 344 (2010)
- Shikonin directly inhibits nitric oxide synthases: possible targets that affect thoracic aorta relaxation response and nitric oxide release from RAW 264.7 macrophages: L.S. Yoshida, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Sci. 112, 343 (2010)
- Shikonin inhibits adipogenesis by modulation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway: H. Lee, et al.; Life Sci. 88, 294 (2011)
- Shikonin and its analogs inhibit cancer cell glycolysis by targeting tumor pyruvate kinase-M2: J. Chen, et al.; Oncogene 30, 4297 (2011)
- Shikonin directly targets mitochondria and causes mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer cells: B. Wiench, et al.; Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2012, 726025 (2012)
- Inhibitory effect of Shikonin on Candida albicans growth: H. Miao, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35, 1956 (2012)
- Topoisomerase I inhibitors, shikonin and topotecan, inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of glioma cells and glioma stem cells: F.L. Zhang, et al.; PLoS One 8, e81815 (2013)
- The anti-tumor effect of shikonin on osteosarcoma by inducing RIP1 and RIP3 dependent necroptosis: Z. Fu, et al.; BMC Cancer 13, 580 (2013)
- Evaluation of radical scavenging properties of shikonin: L.S. Yoshida, et al.; J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 55, 90 (2014)
- Shikonin promotes autophagy in BXPC-3 human pancreatic cancer cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: S. Shi & H. Cao; Oncol. Lett. 8, 1087 (2014)
- The Mechanism Underlying the Antibacterial Activity of Shikonin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Y.S. Lee, et al.; Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2015, 520578 (2015)
- Decreased adiposity and enhanced glucose tolerance in shikonin treated mice: A. Bettaieb, et al.; Obesity 23, 2269 (2015)
- Shikonin Suppresses NLRP3 and AIM2 Inflammasomes by Direct Inhibition of Caspase-1: J. Zorman, et al.; PLoS One 11, e0159826 (2016)
- PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation: M. Xie, et al.; Nat. Commun. 7, 13280 (2016)
- Monoclonal anti-dsDNA antibody 2C10 escorts DNA to intracellular DNA sensors in normal mononuclear cells and stimulates secretion of multiple cytokines implicated in lupus pathogenesis: K. Inoue, et al.; Clin. Exper. Immunol. 199, 150 (2019)
- Structure of Mpro from COVID-19 virus and discovery of its inhibitors: Z. Jin, et al.; Nature (Epub ahead of print) (2020)