Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
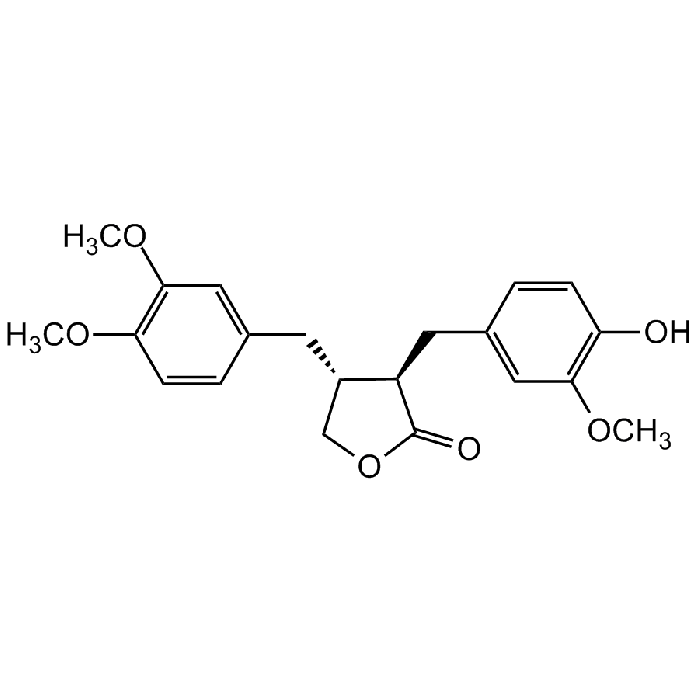
(-)-Arctigenin
As low as
50
CHF
CHF 50.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0530-M01010 mgCHF 50.00
AG-CN2-0530-M05050 mgCHF 150.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (3R,4R)-4-[(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]dihydro-3-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-(3H)-furanone |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C21H24O6 |
| MW | 372.4 |
| CAS | 7770-78-7 |
| RTECS | LY9247000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Semi-synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml). Slightly soluble in ethanol or methanol (both ~1mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR and MS. |
| InChi Key | NQWVSMVXKMHKTF-JKSUJKDBSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C1OC[C@H](CC2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C2)[C@H]1CC3=CC(OC)=C(O)C=C3 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Aglycone metabolite of (-)-Arctiin (AG-CN2-0532), isolated from Arctium lappa.
- Multifunctional natural compound with antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, neuroprotective, antiproliferative and antiviral activities.
- Natural agonist of the PP2A that has potent renoprotective effects in type 1 and type 2 diabetic animal models.
- Inhibits adipogenesis through AMPK induction.
- Modulator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ).
- Inhibits LPS-induced iNOS expression via inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation and p65 nuclear translocation.
- Inhibits NLRP3 in a SIRT1-dependent manner.
- HIV-1 integrase/replication inhibitor in vitro.
- Potently inhibits MKK1 (MEK1).
- Blocks the activation of Akt induced by glucose starvation in pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells. Also dissipates the mitochondrial membrane potential by inhibition of the mitochondrial complexes II and IV. Selectively kills only the OXPHOS-dependent PANC-1 cells. Possibly useful in immunometabolism research.
- Shown to induce cell cycle arrest, autophagy and apoptosis in several cancer cell lines and having chemosensitizing properties.
Product References
- (-)-Arctigenin as a lead structure for inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 integrase: E. Eich, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 39, 86 (1996)
- Identification of arctigenin as an antitumor agent having the ability to eliminate the tolerance of cancer cells to nutrient starvation: S. Awale, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 1751 (2006)
- In vitro anti-inflammatory effects of arctigenin, a lignan from Arctium lappa L., through inhibition on iNOS pathway: F. Zhao, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 122, 457 (2009)
- Arctigenin, a phenylpropanoid dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, inhibits type I-IV allergic inflammation and pro-inflammatory enzymes: J.Y Lee & C.J. Kim; Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 947 (2010)
- Arctigenin, a natural compound, activates AMP-activated protein kinase via inhibition of mitochondria complex I and ameliorates metabolic disorders in ob/ob mice: S.L. Huang, et al.; Diabetologia 55, 1469 (2012)
- Arctigenin preferentially induces tumor cell death under glucose deprivation by inhibiting cellular energy metabolism: Y. Gu, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 84, 468 (2012)
- Arctigenin ameliorates inflammation in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and polarizing M1 macrophages to M2-like macrophages: S.R. Hyam, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 708, 21 (2013)
- Inhibition of angiogenesis: a novel antitumor mechanism of the herbal compound arctigenin: Y. Gu, et al.; Anticancer Drugs 24, 781 (2013)
- Arctigenin effectively ameliorates memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease model mice targeting both β-amyloid production and clearance: Z. Zhu, et al.; J. Neurosci. 33, 13138 (2013)
- (-)-Arctigenin as a lead compound for anticancer agent: G.R. Chen, et al.; Nat. Prod. Res. 27, 2251 (2013)
- Arctigenin Inhibits Adipogenesis by Inducing AMPK Activation and Reduces Weight Gain in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice: Y.H. Han, et al.; J. Cell Biochem. 117, 2067 (2016)
- Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) Isoforms by Arctiin and Arctigenin: H. Zhang, et al.; Phytother. Res. 30, 1189 (2016)
- Arctigenin functions as a selective agonist of estrogen receptor β to restrict mTORC1 activation and consequent Th17 differentiation: X. Wu, et al.; Oncotarget 7, 83893 (2016)
- Mechanistic insights into selective killing of OXPHOS-dependent cancer cells by arctigenin: K. Brecht, et al.; Toxicol. In Vitro 40, 55 (2017)
- Arctigenin, a natural lignan compound, induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human glioma cells: A. Maimaitili, et al.; Oncol. Lett. 13, 1007 (2017)
- Arctigenin attenuates ischemic stroke via SIRT1-dependent inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome: S. Zhang, et al.; BBRC 493, 821 (2017)
- Arctigenin inhibits the activation of the mTOR pathway, resulting in autophagic cell death and decreased ER expression in ER-positive human breast cancer cells: T. Maxwell, et al.; Int. J. Oncol. 52, 1339 (2018)
- Molecular mechanisms of the action of Arctigenin in cancer: Y. He, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 108, 403 (2018) (Review)
- Arctigenin ameliorates renal impairment and inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic db/db mice: J. Zhang, et al.; Life Sci. 223, 194 (2019)
- Arctigenin attenuates diabetic kidney disease through the activation of PP2A in podocytes: Y. Zhong, et al.; Nat. Commun. 10, 4523 (2019)