Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
Pepstatin A
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CP3-7001-M0055 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CP3-7001-M02525 mgCHF 125.00
AG-CP3-7001-M100100 mgCHF 370.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | i-Valeryl-L-Val-L-Val-AHMHA-L-Ala-AHMHA; Procidin S 735A; NSC 272671 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
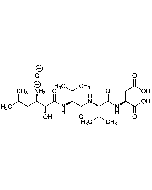
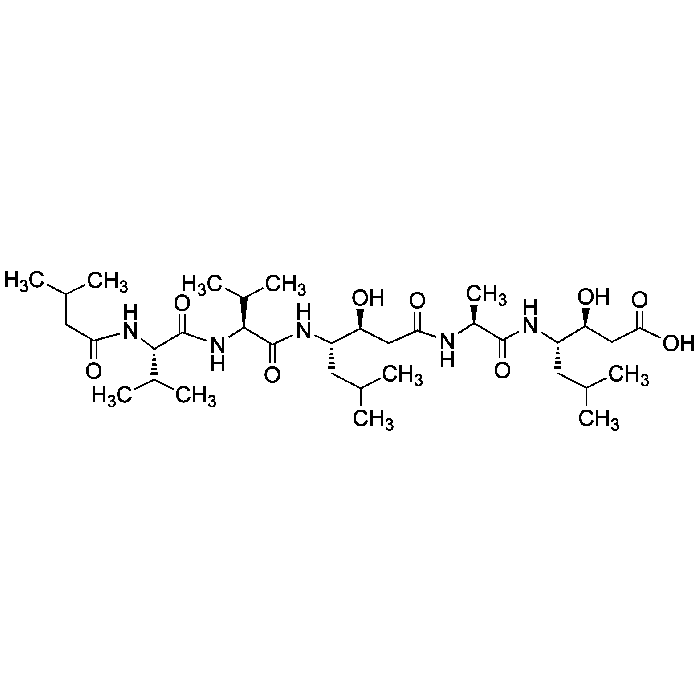
| Formula |
C34H63N5O9 |
| MW | 685.9 |
| Sequence |
Iva-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta |
| Merck Index | 14: 7147 |
| CAS | 26305-03-3 |
| RTECS | SC6155000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), ethanol (1mg/ml, gentle warming), methanol or acetic acid. |
| InChi Key | FAXGPCHRFPCXOO-LXTPJMTPSA-N |
| Smiles | CC(C)C[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CC(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Tight-binding, reversible, highly selective inhibitor of acid proteases (aspartyl peptidases), like pepsin, gastricsin, cathepsin E and D, renin, chymosin, bacterial aspartic proteinases and HIV proteases.
- Does not inhibit thiol proteases, neutral proteases or serine proteases.
- Widely used as a research tool in studies of protease mechanisms and biological functions.
- Solubilized γ-secretase and retroviral protease inhibitor.
- Shows antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic activity.
- Suppresses p53-dependent apoptosis in lymphoid cells as well as TNFα-induced apoptosis in U937 cells.
- Inhibits degradation of autophagic cargo inside autophagolysosomes.
Product References
- Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes: H. Umezawa, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 23, 259 (1970)
- Inhibition of cathepsin D-type proteinase of macrophages by pepstatin, a specific pepsin inhibitor, and other substances: M.H. McAdoo, et al.; Infect. Immun. 7, 655 (1973)
- Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin: J. Jr. Marciniszyn, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7088 (1976)
- Non-specific inhibition of pressor agents in vivo by the renin inhibitor pepstatin A: A.A. Oldham, et al.; J. Hypertens. 2, 157 (1984)
- Inhibition of aspartic proteases by pepstatin and 3-methylstatine derivatives of pepstatin. Evidence for collected-substrate enzyme inhibition: D.H. Rich, et al.; Biochemistry 24, 3165 (1985)
- Inhibition of HIV replication in cell culture by the specific aspartic protease inhibitor pepstatin A: K. von der Helm, et al.; FEBS Lett. 247, 349 (1989)
- Cathepsin D protease mediates programmed cell death induced by interferon-gamma, Fas/APO-1 and TNF-alpha: L.P. Deiss, et al.; EMBO J. 15, 3861 (1996)
- Pepstatin A-sensitive aspartic proteases in lysosome are involved in degradation of the invariant chain and antigen-processing in antigen presenting cells of mice infected with Leishmania major: T. Zhang, et al.; BBRC 276, 693 (2000)
- Linear non-competitive inhibition of solubilized human gamma-secretase by pepstatin A methylester, L685458, sulfonamides, and benzodiazepines: G. Tian, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 31499 (2002)
- Pepstatin A, an aspartic proteinase inhibitor, suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation: H. Yoshida, et al.; J. Biochem. 139, 583 (2006)
- Pepstatin A alters host cell autophagic machinery and leads to a decrease in influenza A virus production: P. Matarrese, et al.; J. Cell Physiol. 226, 3368 (2011)
- Inhibition of XMRV and HIV-1 proteases by pepstatin A and acetyl-pepstatin: K. Matuz, et al.; FEBS J. 279, 3276 (2012)