Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
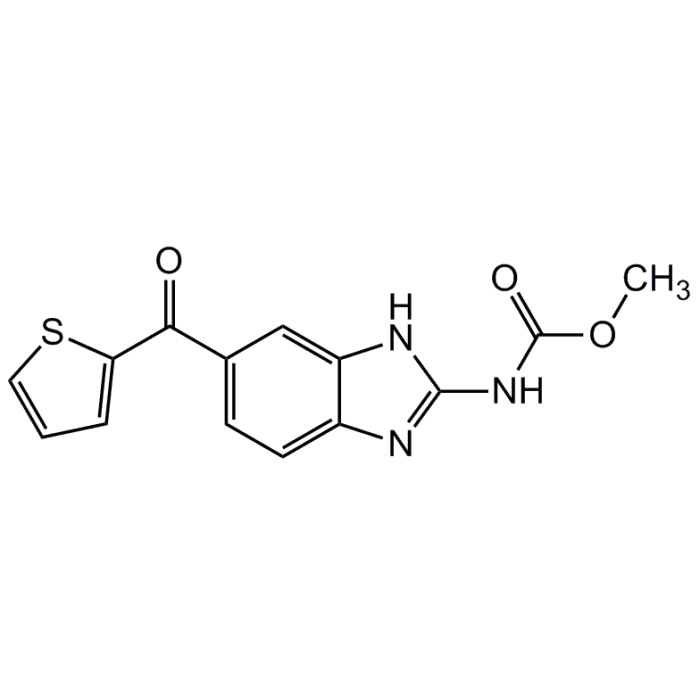
Nocodazole
As low as
45
CHF
CHF 45.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-0019-M0055 mgCHF 45.00
AG-CR1-0019-M01010 mgCHF 70.00
AG-CR1-0019-M02525 mgCHF 125.00
AG-CR1-0019-M05050 mgCHF 230.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Methyl[5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C14H11N3O3S |
| MW | 301.3 |
| CAS | 31430-18-9 |
| RTECS | DD6521000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or dimethylformamide; almost insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | KYRVNWMVYQXFEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | COC(=O)NC1=NC2=CC=C(C=C2N1)C(=O)C1=CC=CS1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Microtubule inhibitor [1, 2, 4].
- Antitumor compound [1, 2].
- Mitosis inhibitor [3].
- Arrests the cell cycle at G2/M phase [9].
- Promotes tubulin depolymerization [4].
- Induces fragmentation of the Golgi complex [5].
- Inhibits the T cell antigen receptor [6].
- Stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of tubulin [7].
- Activates the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway [8].
- Apoptosis inducer [10, 11].
- Autophagy inhibition through prevention of autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
Product References
- R17934-NSC 238159: a new antitumor drug--I. Effect on experimental tumors and factors influencing effectiveness: G. Atassi and H.J. Tagnon; Eur. J. Cancer 11, 599 (1975)
- R17934-NSC238159: a new antitumor drug--II. Effect on mitotic cycle of L1210 leukemia cells in vivo and synergism with cytosine arabinoside (NSC63878): G. Atassi, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 11, 609 (1975)
- Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis; M.A. Jordan, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 102, 401 (1992)
- Nanomolar concentrations of nocodazole alter microtubule dynamic instability in vivo and in vitro: R.J. Vasquez, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 8, 973 (1997)
- Recycling of golgi-resident glycosyltransferases through the ER reveals a novel pathway and provides an explanation for nocodazole-induced Golgi scattering: B. Storrie, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 143, 1505 (1998)
- Nocodazole inhibits signal transduction by the T cell antigen receptor: R.D. Huby, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12024 (1998)
- Studies on the nocodazole-induced GTPase activity of tubulin: M.R. Mejillano, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 336, 130 (1996)
- Microtubule-interfering agents activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase through both Ras and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase pathways: T.H. Wang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4928 (1998)
- Raf-1/MEK/MAPK pathway is necessary for the G2/M transition induced by nocodazole: C. Hayne, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 31876 (2000)
- Apoptosis induced by microtubule disrupting drugs in normal murine thymocytes in vitro: V. Bumbasirevic, et al.; Scanning Microsc. 9, 509 (1995)
- Nocodazole induces mitotic cell death with apoptotic-like features in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: K. Endo, et al.; FEBS Lett. 584, 2387 (2010)





