Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
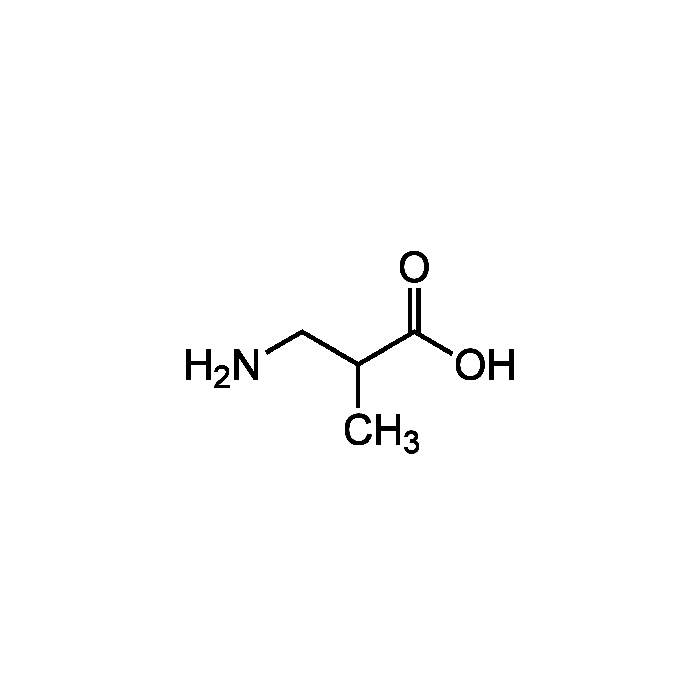
3-Aminoisobutyric acid
As low as
55
CHF
CHF 55.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3596-M250250 mgCHF 55.00
AG-CR1-3596-G0011 gCHF 130.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | β-Aminoisobutyric acid; BAIBA; 3-Amino-2-methylpropanoic acid; DL-3-Aminoisobutyric acid; α-Methyl-β-alanine; 3-Aminoisobutanoate; 3-Aminoisobutyrate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C4H9NO2 . H2O |
| MW | 103.1 . 18.0 |
| CAS | 214139-20-5 and 144-90-1 (anhydrous) |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (TLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO or water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| InChi Key | QCHPKSFMDHPSNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CC(CN)C(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Catabolite of thymine [1-4].
- Precursor for 3-Hydroxyisobutyric acid synthesis [3].
- Small molecule myokine. Browning inducer of white adipose tissue (WAT) into brown adipose tissue (BAT) [9, 10].
- PGC-1α-mediated and exercise-triggered nonadrenergic activator of the thermogenic program in WAT. Increases the expression of brown adipocyte-specific genes (browning) in white adipocytes and β-oxidation in hepatocytes through a PPARα-mediated mechanism [9, 10].
- Induces a brown adipose-like phenotype in human pluripotent stem cells and improves glucose homeostasis [9, 10].
- Enhances fatty acid oxidation and reduces body weight in mice through an increased production of leptin by the white adipose tissue (WAT) [5-7].
- Inhibits Agxt2-mediated metabolism of dimethylarginines [8].
- Partial agonist of the glycine receptor (GlyR) [4].
Product References
- beta-Aminoisobutyric acid (alpha-methyl-beta-alanine); a new amino-acid obtained from human urine: H.R. Crumpler, et al.; Nature 167, 307 (1951)
- beta-aminoisobutyric acid, a new probe for the metabolism of DNA and RNA in normal and tumorous tissue: H.R. Nielsen, et al.; Cancer Res. 34, 1381 (1974)
- Metabolism of thymine in tumor tissue: the origins of beta-aminoisobutyric acid: B.S. Baliga & E. Borek; Adv. Enzyme Regul. 13, 27 (1975)
Accumulation of 3-hydroxyisobutyric acid, 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyric acid and 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid in ketoacidosis: S. Landaas; Clin. Chim. Acta 64, 143 (1975) - Pharmacology of the inhibitory glycine receptor: agonist and antagonist actions of amino acids and piperidine carboxylic acid compounds: V. Schmieden & H. Betz; Mol. Pharmacol. 48, 919 (1995)
- Effects of zidovudine, stavudine and beta-aminoisobutyric acid on lipid homeostasis in mice: possible role in human fat wasting: C. Maisonneuve, et al.; Antivir. Ther. 9, 801 (2004)
- Beta-aminoisobutyric acid prevents diet-induced obesity in mice with partial leptin deficiency: K. Begriche, et al.; Obesity (Silver Spring) 16, 2053 (2008)
- Effects of beta-aminoisobutyric acid on leptin production and lipid homeostasis: mechanisms and possible relevance for the prevention of obesity: K. Begriche, et al.; Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 24, 269 (2010)
- In vivo evidence that Agxt2 can regulate plasma levels of dimethylarginines in mice: A. Kittel, et al.; BBRC 430, 84 (2013)
- beta-Aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic beta-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors: L.D. Roberts, et al.; Cell Metab. 19, 96 (2014)
- Come on BAIBA light my fire: H.L. Kammon & M. Febbraio; Cell Metab. 19, 1 (2014) (Review)
- BAIBA attenuates insulin resistance and inflammation induced by palmitate or a high fat diet via an AMPK–PPARδ-dependent pathway in mice: TW. Jung, et al.; Diabetologia 58, 2096 (2015)
- Dynamic of lipid droplets and gene expression in response to β-aminoisobutyric acid treatment on 3T3-L1 cells: M. Colitti, et al.; Eur. J. Histochem. 62, 2984 (2018)
- The L-enantiomer of β-aminobutyric acid (L-BAIBA) as a potential marker of bone mineral density, body mass index, while D-BAIBA of physical performance and age: Ch. Lyssikatos, et al. Res. Square doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2492688/v1 (2023)