Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
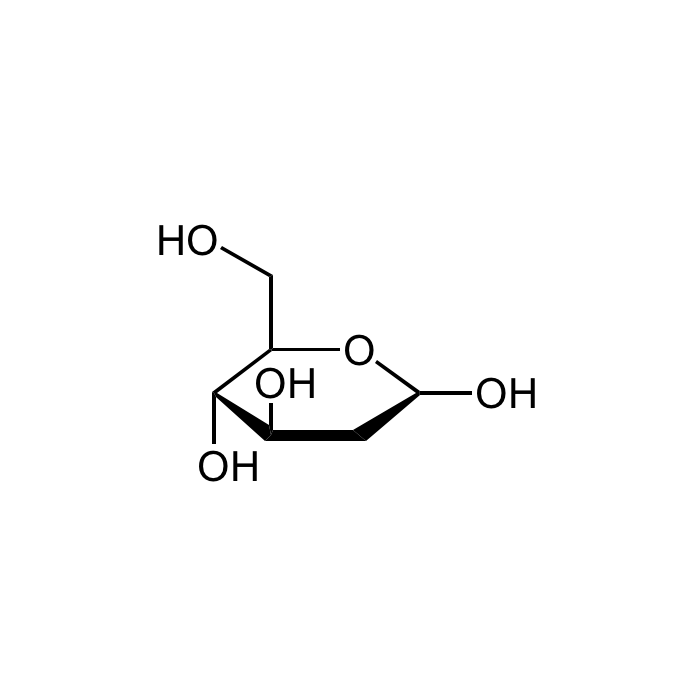
2-Deoxy-D-glucose
As low as
65
CHF
CHF 65.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3681-G0011 gCHF 65.00
AG-CR1-3681-G0055 gCHF 240.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 2-Deoxyglucose; 2-Deoxy-D-arabinohexose; Ba2758; NSC 15293; 2-DG |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C6H12O5 |
| MW | 164.2 |
| CAS | 154-17-6 |
| RTECS | MQ3325000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), DMF or water (10mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Other Product Data |
Optical Rotation [α]D20 (c=1, water): +44.0° to +48.0°. |
| InChi Key | PMMURAAUARKVCB-KAZBKCHUSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1C[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Non-metabolizable glucose analog.
- An indirect inhibitor of hexokinase (HK), inhibiting the rate limiting step of glycolysis and consequently decreases glycolysis. Inhibits phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase, which consequently results in the depletion in cellular ATP, the inhibition of protein glycosylation and the disruption of ER quality control by inducing the unfolded protein response.
- Useful agent for immunometabolism research.
- Anticancer agent. Shown to cause in vitro cell cycle inhibition and cell death in models of hypoxia, induce autophagy, increase reactive oxygen species production, activate AMPK and block tumor cell growth in animal models.
- Potential antiviral agent. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) is potentially useful for COVID-19 treatment due to its effects on the glycolytic pathway, antiinflammatory activity and interaction with viral proteins. 2-DG has previously been shown to be effective against other viruses in cell culture. Blocking glycolysis with non-toxic concentrations of 2-deoxy-D-glucose prevented SARS-CoV-2 replication and viral growth in Caco-2 cells.
Product References
- Competitive inhibition of rat brain hexokinase by 2-deoxyglucose, glucosamine, and metrizamide: J.M. Bertoni; J. Neurochem. 37, 1523 (1981)
- Insulin binds to specific receptors and stimulates 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in cultured glial cells from rat brain: D.W. Clarke, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 259, 11672 (1984)
- 2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibition of herpes simplex virus type-1 receptor expression: J.G. Mohanty & K.S. Rosenthal; Antiviral Res. 6, 137 (1986)
- Greater cell cycle inhibition and cytotoxicity induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose in tumor cells treated under hypoxic vs aerobic conditions: J.C. Maher, et al; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 53, 116 (2004)
- 2-deoxyglucose: an anticancer and antiviral therapeutic, but not any more a low glucose mimetic: H.T. Kang & E.S. Hwang; Life Sci. 78, 1392 (2006)
- Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on various malignant cell lines in vitro: X.D. Zhang, et al.; Anticancer Res. 26, 3561 (2006)
- Under normoxia, 2-deoxy-D-glucose elicits cell death in select tumor types not by inhibition of glycolysis but by interfering with N-linked glycosylation: M. Kurtoglu, et al.; Mol. Cancer Therap. 6, 3049 (2007)
- A catabolic block does not sufficiently explain how 2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibits cell growth: M. Ralser, et al.; PNAS 105, 17807 (2008)
- 2-deoxy-D-glucose as a potential drug against fusogenic viruses including HIV: G.E. Parris; Med. Hypotheses 70, 776 (2008)
- Protection of normal cells and tissues during radio- and chemosensitization of tumors by 2-deoxy-D-glucose: A. Farooque, et al.; J. Cancer Res. Ther. 1, S32 (2009) (Review)
- Targeting glucose metabolism with 2-deoxy-D-glucose for improving cancer therapy: B. Dwarakanath & V. Jain; Future Oncol. 5, 581 (2009) (Review)
- 2-Deoxy-D-glucose activates autophagy via endoplasmic reticulum stress rather than ATP depletion: H. Xi, et al.; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 67, 899 (2011)
- Hexokinase II acts through UCP3 to suppress mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production and maintain aerobic respiration: R.J. Mailloux, et al.; Biochem. J. 437, 301 (2011)
- 2-Deoxy-D-glucose targeting of glucose metabolism in cancer cells as a potential therapy: D. Zhang, et al.; Cancer Lett. 355, 176 (2014) (Review)
- A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016) (Review)
- 2-deoxy-d-glucose Ameliorates Animal Models of Dermatitis: S.Y. Choi, et al.; Biomedicines 8, 20 (2020)
- Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets: D. Bojkova, et al.; Nature 583, 469 (2020)
- A combinatorial approach of a polypharmacological adjuvant 2-deoxy-D-glucose with low dose radiation therapy to quell the cytokine storm in COVID-19 management: A. Verma, et al.; Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 96, 1323 (2020)