Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
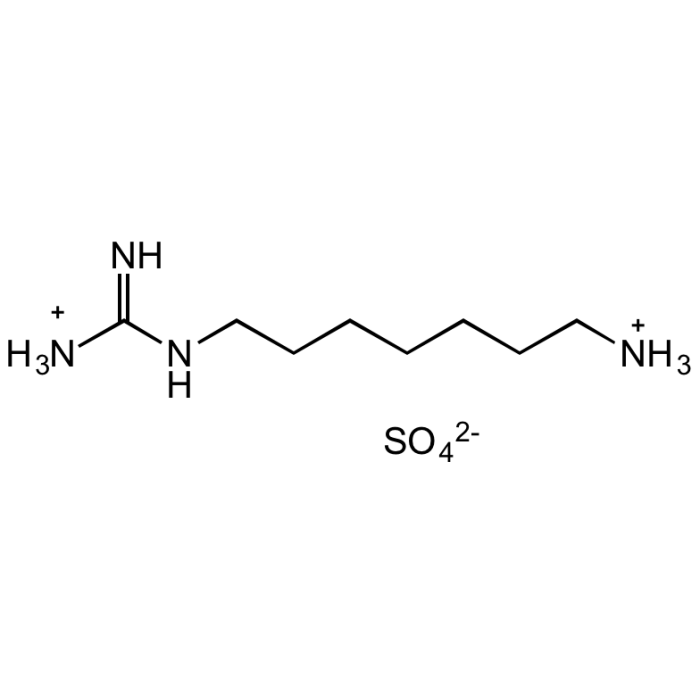
N1-Guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane [GC7]
As low as
140
CHF
CHF 140.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3702-M01010 mgCHF 140.00
AG-CR1-3702-M05050 mgCHF 420.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C8H22N4O4S |
| MW | 270.0 |
| CAS | 150417-90-6 (parent 150333-69-0) |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (1H-NMR) |
| Purity Detail | This product is di-guanyl aminoheptane free. |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetic acid. See also Solubility Note below. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR |
| Other Product Data |
Solubility Note: 1. Prepare fresh a solution of 10 mM acetic acid (28.6 µl concentrated acetic acid [17.5 M] in 50 ml H2O). 2. Prepare a fresh stock solution of GC7 by dissolving it in 10 mM acetic acid to prevent precipitation from atmospheric CO2. 3. Prepare a working solution by further dissolving in culture medium to the required concentration. 4. When GC7 is used for cell culture it should be used together with 0.5 mM aminoguanidine to prevent destruction of monoamine oxidase (see Chen 1996). |
| InChi Key | MDDOWYFCKAAANU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | [NH3+]C(NCCCCCCC[NH3+])=N.O=S([O-])([O-])=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep cool and dry. Protect from moisture and oxygen. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable competitive deoxyhypusine synthase (DHPS) inhibitor. Targets the spermidine-binding site of deoxyhypusine synthase (Ki = 9.7 nM), and prevents the first step in the post-translational conversion of a single lysine to hypusine on eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A). The modification is essential for sustained cell growth and therefore eIF5A hypusination controls cell proliferation and has been linked to cancer.
- Hypusination of eIF-5aA in macrophages is required for the TCA/OXPHOS pathways by regulating the expression of the important enzymes of the pathways. GC7 blocks the expression of the key enzymes (at the level of translation) and blocks OXPHOS in macrophages.
- Useful tool for immunometabolism research.
- The polyamine spermidine as a substrate to generate hypusinated eIF5A. Elevated levels of polyamines are a hallmark of most tumor types. Agents that block the function of key biosynthetic enzymes in the polyamine pathway markedly impair tumor progression and maintenance of the malignant state.
- Anti-tumor agent in vivo. Anti-proliferative agent in several solid tumors. Shown to increase the chemosensitivity to other anticancer drugs.
- Inhibits HIF-1α expression and activates autophagy independent of DHPS.
- Inhibition of deoxyhypusine synthase may provide a strategy for reducing diabetogenic Th1 cells and preserving β cell function in type 1 diabetes.
- Hypusinated eIF5A has been demonstrated to have a proinflammatory role in the release of cytokines and the production of NO and might be an interesting cellular target for anti-inflammatory treatments.
Product References
- Features of the spermidine-binding site of deoxyhypusine synthase as derived from inhibition studies. Effective inhibition by bis- and mono-guanylated diamines and polyamines: J. Jakus, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13151 (1993)
- Diamine and triamine analogs and derivatives as inhibitors of deoxyhypusine synthase: synthesis and biological activity: Y.B. Lee, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 38, 3053 (1995)
- Effects of inhibitors of deoxyhypusine synthase on the differentiation of mouse neuroblastoma and erythroleukemia cells: Z.P. Chen, et al.; Cancer Lett. 105, 233 (1996)
- Effects of N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane, an inhibitor of deoxyhypusine synthase, on the growth of tumorigenic cell lines in culture: X.P. Shi, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1310, 119 (1996)
- Cell cycle arrest in archaea by the hypusination inhibitor N(1)-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane: B.P. Jansson, et al.; J. Bacteriol. 182, 1158 (2000)
- Effect of N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane, an inhibitor of deoxyhypusine synthase, on endothelial cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis: Y. Lee, et al.; Mol. Cell Biochem. 237, 69 (2002)
- Inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) hypusination impairs melanoma growth: M.G. Jasiulionis, et al.; Cell Biochem. Funct. 25, 109 (2007)
- Inhibition of deoxyhypusine synthase enhances islet {beta} cell function and survival in the setting of endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes: R.D. Robbins, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 39943 (2010)
- Prognostic significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma: N.P. Lee, et al.; Int. J. Cancer 127, 968 (2010)
- Deoxyhypusine synthase promotes differentiation and proliferation of T helper type 1 (Th1) cells in autoimmune diabetes: S.C. Colvin, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 288, 36226 (2013)
- Hypusine modification of the ribosome-binding protein eIF5A, a target for new anti-inflammatory drugs: understanding the action of the inhibitor GC7 on a murine macrophage cell line: O.P. de Almeida, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 20, 284 (2014) (Review)
- The spermidine analogue GC7 (N1-guanyl-1,7-diamineoheptane) induces autophagy through a mechanism not involving the hypusination of eIF5A: S. Oliverio, et al.; Amino Acids 46, 2767 (2014)
- Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) is essential for HIF-1α activation in hypoxia: M. Tariq, et al.; BBRC 470, 417 (2016)
- Targeting the polyamine-hypusine circuit for the prevention and treatment of cancer: S. Nakanishi & J.L. Cleveland; Amino Acids 48, 2353 (2016) (Review)
- N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane enhances the chemosensitivity of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to vincristine through inhibition of eif5a-2 activation: Y. Liu, et al.; Anticancer Drugs 28, 1097 (2017)
- Targeting eIF5A hypusination prevents anoxic cell death through mitochondrial silencing and improves kidney transplant outcome: N. Melis, et al.; J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 811 (2017)
- Polyamines and eIF5A hypusination modulate mitochondrial respiration and macrophage activation: D.J. Puleston, et al.; Cell Metabol. (Epub ahead of Print) (2019)





