Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
PD 0325901
As low as
30
CHF
CHF 30.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3711-M0011 mgCHF 30.00
AG-CR1-3711-M0055 mgCHF 70.00
AG-CR1-3711-M02525 mgCHF 190.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
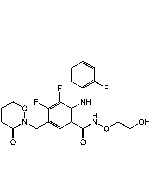
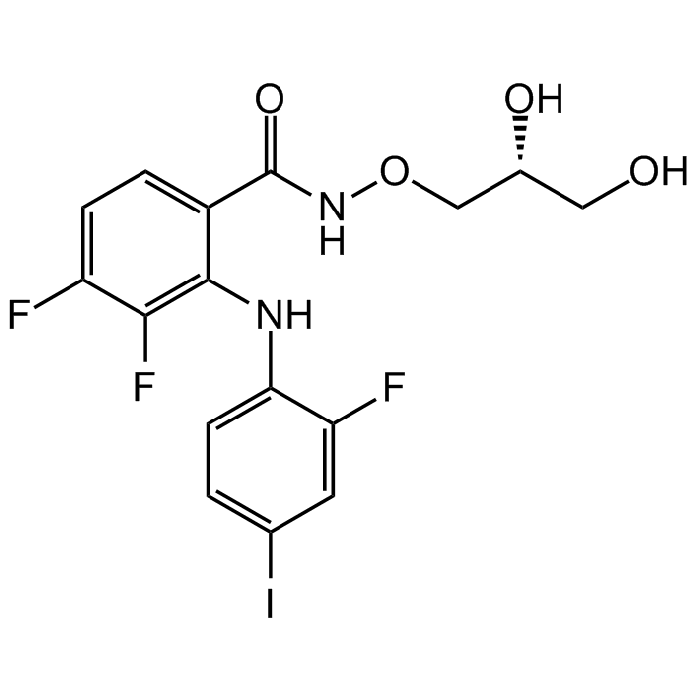
| Synonyms | Mirdametinib; N-[(2R)-2,3-Dihydroxypropoxy]-3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]-benzamide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C16H14F3IN2O4 |
| MW | 482.2 |
| CAS | 391210-10-9 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or ethanol (15mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | SUDAHWBOROXANE-SECBINFHSA-N |
| Smiles | FC1=CC=C(C(NOC[C@H](O)CO)=O)C(NC2=CC=C(I)C=C2F)=C1F |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- PD 0325901 is a potent and selective non-ATP competitive orally active MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitor. In comparison to the CI-1040 MEK inhibitor, PD 0325901 has a greater potency of inhibition, longer duration, greater solubility, improved bioavailability and increased metabolic stability. The dual specific threonine/tyrosine kinase MEK is a key component of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway that is frequently activated in human tumors. This cell permeable inhibitor of the MEK/ERK pathway inhibits the activation and downstream signaling of MEK.
- PD 0325901 is an anti-cancer agent that is highly effective at inhibiting cell growth and proliferation in various cancer cells. It has been shown to inhibit MEK activity and suppresses phosphorylation of ERK in mouse colon 26 cells (IC50 = 0.33nM) and the growth of melanoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. It induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a mouse xenograft model and inhibits production of proangiogenic cytokines such as VEGF. This derivative of MEK inhibitor CI-1040 is 500-fold more potent than CI-1040 on phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2.
- PD 0325901 promotes reprogramming of human somatic cells to iPSCs and enhances generation and self-renewal of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in combination with other compounds.
Product References
- The biological profile of PD 0325901: a second generation analog of CI-1040 with improved pharmaceutical potential: J.S. Sebolt-Leopold, et al.; Proc. Amer. Assoc. Cancer Res. 45, 925 (2004)
- The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update: J. Bain, et al.; Biochem. J. 408, 297 (2007)
- The discovery of the benzhydroxamate MEK inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901: S.D. Barrett, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 6501 (2008)
- The ground state of embryonic stem cell self-renewal: Q.L. Ying, et al.; Nature 453, 519 (2008)
- Promotion of reprogramming to ground state pluripotency by signal inhibition: J. Silva, et al.; PLoS Biol. 6, e253 (2008)
- Growth-inhibitor and antiangiogenic activity of the MEK inhibitor PD0325901 in malignant melanoma with or without BRAF mutations: L. Ciuffreda, et al.; Neoplasia 11, 720 (2009)
- A chemical platform for improved induction of human iPSCs: T. Lin, et al.; Nat. Methods 6, 805 (2009)
- Reprogramming of human primary somatic cells by OCT4 and chemical compounds: S. Zhu, et al.; Cell Stem Cell 7, 621 (2010)
- Maintenance of Self-Renewal and Pluripotency in J1 Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells through Regulating Transcription Factor and MicroRNA Expression Induced by PD0325901: Z. Ai, et al.; Stem Cells Int. 2016, 1792573 (2016)
- MEK inhibitor PD0325901 and vitamin C synergistically induce hypomethylation of mouse embryonic stem cells: C. Li, et al.; Oncotarget 7, 39730 (2016)
- RAF dimer inhibition enhances the antitumor activity of MEK inhibitors in K-RAS mutant tumors: X. Yuan, et al.; Mol. Oncol. 14, 1833 (2020)