Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
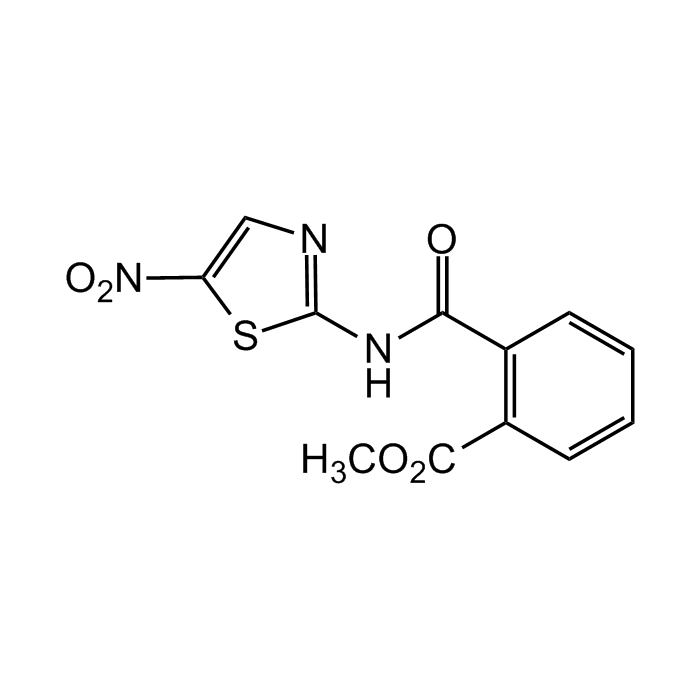
Nitazoxanide
As low as
50
CHF
CHF 50.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3723-M01010 mgCHF 50.00
AG-CR1-3723-M05050 mgCHF 80.00
AG-CR1-3723-M250250 mgCHF 290.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 2-(Acetyloxy)-N-(5-nitro-2-thiazolyl)benzamide; NSC 697855; NTZ |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C12H9N3O5S |
| MW | 307.3 |
| CAS | 55981-09-4 |
| RTECS | VN7830000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | GMMVCIKWTYKLKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(NC1=NC=C([N+]([O-])=O)S1)C2=C(C(OC)=O)C=CC=C2 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Nitazoxanide is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic, antimicrobial and antiviral drug that is used in medicine for the treatment of various helminthic, protozoal, bacterial and viral infections.
- Nitazoxanide is rapidly metabolized to tizaxonide, an antiparasitic drug of the thiazolide class. The anti-protozoal activity and activity against anaerobic bacteria is believed to be due to interference with the pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) enzyme-dependent electron transfer reaction which is essential to anaerobic energy metabolism. Nitazoxanide also showed a variety of other antibacterial mechanisms, inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase in E. coli, disrupting the membrane potential and pH homeostasis in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis and suppressing the chaperone/usher (CU) pathway of the Gram-negative bacteria.
- It is being studied for potential treatment for chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, rotavirus, norovirus gastroenteritis and the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The mechanism is suppressing the viral replication by inhibiting maturation of the viral hemagglutinin and the viral transcription factor immediate early 2 (IE2) as well as by activating the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (an antiviral intracellular protein).
- Nitazoxanide modulates a variety of other pathways in vitro, including glutathione-S-transferase and glutamate-gated chloride ion channels in nematodes, respiration and other pathways in bacteria and cancer cells and viral and host transcriptional factors.
- Nitazoxanide has also been shown to be a potent antagonist of the Ca2+-activated Cl- channel TMEM16A, which offers a new mechanism to bronchodilate airways and block the multiple contractiles operating in severe diseases.
Product References
- Nitazoxanide: a new thiazolide antiparasitic agent: L.M. Fox & L.D. Saravolatz; Clin. Infect. Dis. 40, 1173 (2005) (Review)
- Antiparasitic drug nitazoxanide inhibits the pyruvate oxidoreductases of Helicobacter pylori, selected anaerobic bacteria and parasites, and Campylobacter jejuni: P.S. Hoffman, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 868 (2007) (Review)
- Thiazolides, a New Class of Anti-Influenza Molecules Targeting Viral Hemagglutinin at the Post-Translational Level: J.F. Rossignol, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 284, 29798 (2009)
- Nitazoxanide kills replicating and nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis and evades resistance: L.P. de Carvalho, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 52, 5789 (2009) (Review)
- Nitazoxanide inhibits biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis by blocking accumulation on surfaces: F. Tchouaffi-Nana, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 2767 (2010) (Review)
- Nitazoxanide, an antiviral thiazolide, depletes ATP-sensitive intracellular Ca(2+) stores: O. Ashiru, et al.; Virology 462-463, 135 (2014) (Review)
- Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent: J.F. Rossignol; Antiviral Res. 110, 94 (2014) (Review)
- Nitazoxanide, a new drug candidate for the treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: J.F. Rossignol; J. Infect. Public Health 9, 227 (2016) (Review)
- Update on Nitazoxanide: A Multifunctional Chemotherapeutic Agent: A. Shakya, et al.; Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 15, 201 (2018) (Review)
- Nitazoxanide, an antiprotozoal drug, inhibits late-stage autophagy and promotes ING1-induced cell cycle arrest in glioblastoma: X. Wang, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 9, 1032 (2018) (Review)
- Drug Repurposing: The Anthelmintics Niclosamide and Nitazoxanide Are Potent TMEM16A Antagonists That Fully Bronchodilate Airways: K. Miner, et al.; Front. Pharmacol. 10, 51 (2019) (Review)
- The FDA-Approved Oral Drug Nitazoxanide Amplifies Host Antiviral Responses and Inhibits Ebola Virus: L.D. Jasenosky, et al.; iScience 19, 1279 (2019) (Review)
- Astrovirus Replication Is Inhibited by Nitazoxanide In Vitro and In Vivo: V. Hargest, et al.; J. Virol. 94, e01706 (2020) (Review)
- Research and Development on Therapeutic Agents and Vaccines for COVID-19 and Related Human Coronavirus Diseases: C. Liu, et al.; ACS Cent. Sci. 6, 315 (2020)