Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
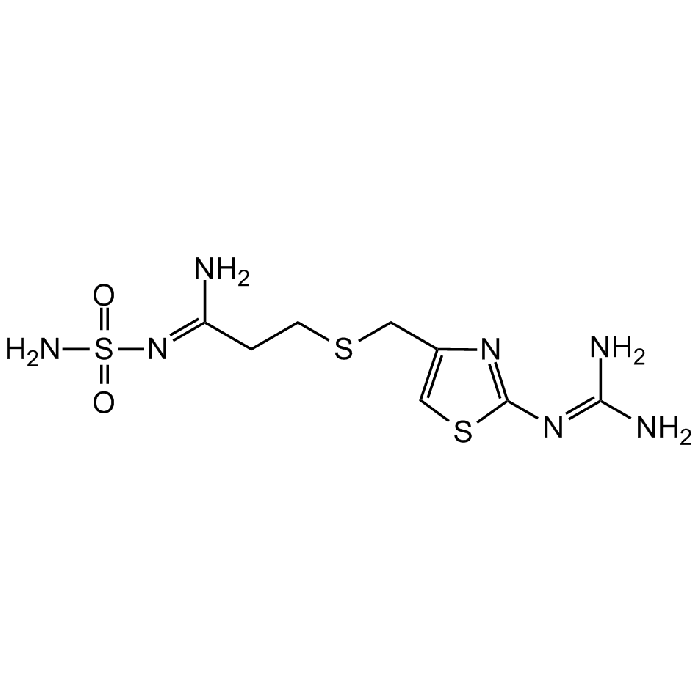
Famotidine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MK-208; YM-11170; Pepcid; N′-(Aminosulfonyl)-3-([2-(diaminomethyleneamino)-4-thiazolyl]methylthio)propanamidine |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C8H15N7O2S3 |
| MW | 337.5 |
| CAS | 76824-35-6 |
| RTECS | UA2300000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (30mg/ml) or DMF (30mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | XUFQPHANEAPEMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | N/C(N)=N/C1=NC(CSCC/C(N)=N/S(=O)(N)=O)=CS1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
-
Famotidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist. It is selective for H2 over H1 and muscarinic receptors (Kis = 4 and 28 µM, respectively, in bovine cerebral cortex).
-
Famotidine blocks the action of histamine in the parietal cells, ultimately blocking acid secretion in the stomach. It inhibits histamine-induced acid secretion in isolated canine parietal cells (IC50 = 0.6µM) and suppresses histamine-induced gastric acid secretion in dogs when administered orally and in anesthetized rats when administered intraduodenally (ID50s = 10 and 400µg/kg, respectively).
-
Famotidine is used to treat ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and heartburn and it decreases the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
-
Potential inhibitor of the viral enzyme papain-like protease (PLpro), important for SARS-CoV-2 replication and being tested in COVID-19 clinical trials.
- Pharmacokinetics of famotidine, a new H2-receptor antagonist, in relation to renal function: T. Takabatake, et al.; Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28, 327 (1985)
- Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: Quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay: N. Kubo, et al.; Jap. J. Pharmacol 43, 277 (1987)
- Famotidine. An updated review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in peptic ulcer disease and other allied diseases: H.D. Langtry, et al.; Drugs 38, 551 (1989) (Review)
- Differences in the antisecretory actions of the proton pump inhibitor AG-1749 (lansoprazole) and the histamine H2-receptor antagonist famotidine in rats and dogs: H. Nagaya, et al.; Jap. J. Pharmacol. 55, 425 (1991)
- Clinical pharmacokinetics of famotidine: H. Echizen & T. Ishizaki; Clin. Pharmacokinet. 21, 178 (1991) (Review)
- Famotidine, the new antiulcero-genic agent, a potent ligand for metal ions: H. Kozlowski, et al.; J. Inorg. Biochem. 48, 233 (1992)
- Famotidine in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): I.C. Wesdorp; Hepatogastroenterology 1, 24 (1992) (Review)
- Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods: C. Wu, et al.; Acta Pharm. Sin. B. (Epub ahea of print) (2020)