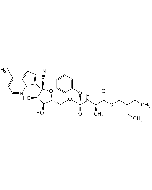Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
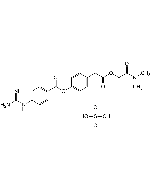
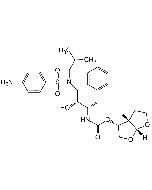
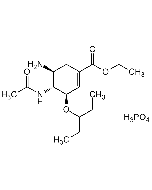
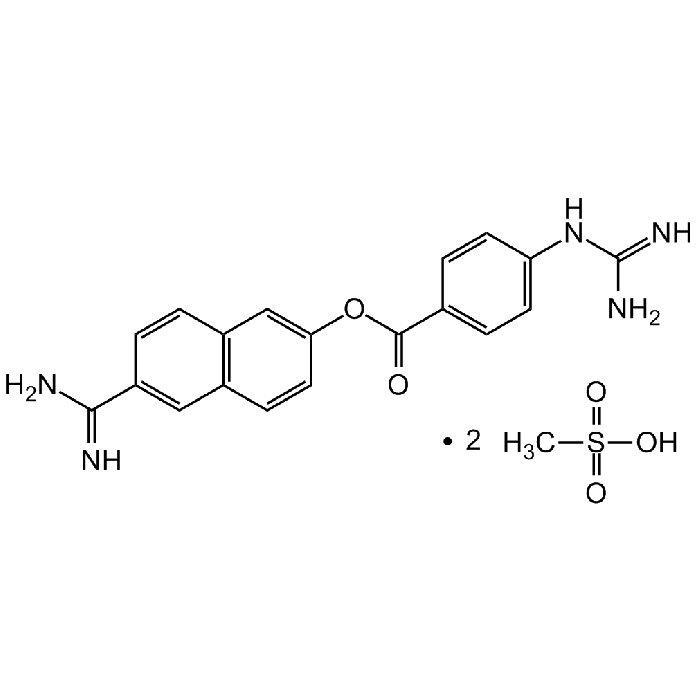
Nafamostat . mesylate
As low as
60
CHF
CHF 60.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CR1-3731-M01010 mgCHF 60.00
AG-CR1-3731-M05050 mgCHF 180.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Nafamastat; Coahibitor; FUT-175; Futhan; 6-Amidino-2-naphthyl p-guanidinobenzoate dimethanesulfonate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C19H17N5O2 . 2CH4O3S |
| MW | 347.4 . 192.2 |
| CAS | 82956-11-4 |
| RTECS | DG2736000 |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml) or water (25mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | SRXKIZXIRHMPFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | NC(C1=CC2=C(C=C1)C=C(OC(C3=CC=C(NC(N)=N)C=C3)=O)C=C2)=N.CS(=O)(O)=O.CS(=O)(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Nafamostat mesylate is a cell permeable broad spectrum potent and reversible synthetic serine protease inhibitor and kallikrein inhibitor in vitro and in vivo.
- It inhibits trypsin (Ki=15nM), tryptase (Ki=95.3pM) and additional proteases in the coagulation cascade including thrombin (Ki=0.84µM).
- Nafamostat mesylate is a short-acting anticoagulant with anti-inflammatory, anticancer and antiviral properties.
- As a potential anticancer agent, it blocks canonical NF-κB signaling, targets TNFR1-stimulated cleavage of caspase families and the tryptase of mast cells to improve therapeutic outcome and to ameliorate cancer therapy resistance and avoid immune resistance.
- It has been shown to reduce eosinophil infiltration, mast cell activation and airway responsiveness in a murine model of asthma.
- Inhibits the demethylase activity of the fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO).
- As antiviral agent, it inhibits Ebola virus, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro and potentially the spread of COVID-19.
- Nafamostat mesylate inhibits TMPRSS2-dependent host cell entry of MERS-CoV. It is also an inhibitor of the enzyme transmembrane serine protease TMPRSS2 and blocks the entry of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) into lung cells in vitro, with roughly 15-fold higher efficiency than Camostat mesylate (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3716), with an EC50 in the low nanomolar range.
Product References
- Inhibitory effect of nafamostat mesilate on metastasis into the livers of mice and on invasion of the extracellular matrix by cancer cells: T. Kimura, et al.; J. Int. Med. Res. 20, 343 (1992)
- Anticoagulation with nafamostat mesilate, a synthetic protease inhibitor, in hemodialysis patients with a bleeding risk: T. Matsuo, et al.; Haemostasis 23, 135 (1993)
- Nafamostat mesilate, a broad spectrum protease inhibitor, modulates platelet, neutrophil and contact activation in simulated extracorporeal circulation: S. Sundaram, et al.; Thromb. Haemost. 75, 76 (1996)
- Inhibitory mechanism of human platelet aggregation by nafamostat mesilate: I Fuse, et al.; Platelets 10, 212 (1999)
- Nafamostat mesilate, a serine protease inhibitor, suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide synthesis and apoptosis in cultured human trophoblasts: M. Nakatsuka, et al.; Life Sci. 67, 1243 (2000)
- Nafamostat mesilate is an extremely potent inhibitor of human tryptase: S. Mori, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Sci. 92, 420 (2003)
- Antitumor effects of Nafamostat mesilate on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Y. Yamashita, et al.; Auris Nasus Larynx. 34, 487 (2007)
- Nafamostat mesilate, a potent serine protease inhibitor, inhibits airway eosinophilic inflammation and airway epithelial remodeling in a murine model of allergic asthma: M. Ishizaki, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Sci. 108, 355 (2008)
- Anti-tumor effect by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation using nafamostat mesilate for pancreatic cancer in a mouse model: K. Furukawa, et al.; Oncol. Rep. 24, 843 (2010)
- A Synthetic Serine Protease Inhibitor, Nafamostat Mesilate, Is a Drug Potentially Applicable to the Treatment of Ebola Virus Disease: H. Nishimura & M. Yamaya; Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 237, 45 (2015)
- Inhibition of the NF-κB pathway by nafamostat mesilate suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis: Y.X. Lu, et al.; Cancer Lett. 380, 87 (2016)
- Identification of Nafamostat as a Potent Inhibitor of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus S Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion Using the Split-Protein-Based Cell-Cell Fusion Assay: M. Yamamoto, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 6532 (2016)
- Nafamostat mesilate, a serine protease inhibitor, suppresses interferon-gamma-induced up-regulation of programmed cell death ligand 1 in human cancer cells: S. Homma, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 54, 39 (2018)
- Identification of nafamostat mesilate as an inhibitor of the fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) demethylase activity: X. Han, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 297, 80 (2019)
- The Molecular Aspect of Antitumor Effects of Protease Inhibitor Nafamostat Mesylate and Its Role in Potential Clinical Applications: X. Chen, et al.; Front. Oncol. 9, 852 (2019) (Review)
- Nafamostat mesylate blocks activation of SARS-CoV-2: New treatment option for COVID-19: M. Hoffmann, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. (Epub ahead of print) (2020)