Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
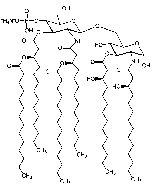
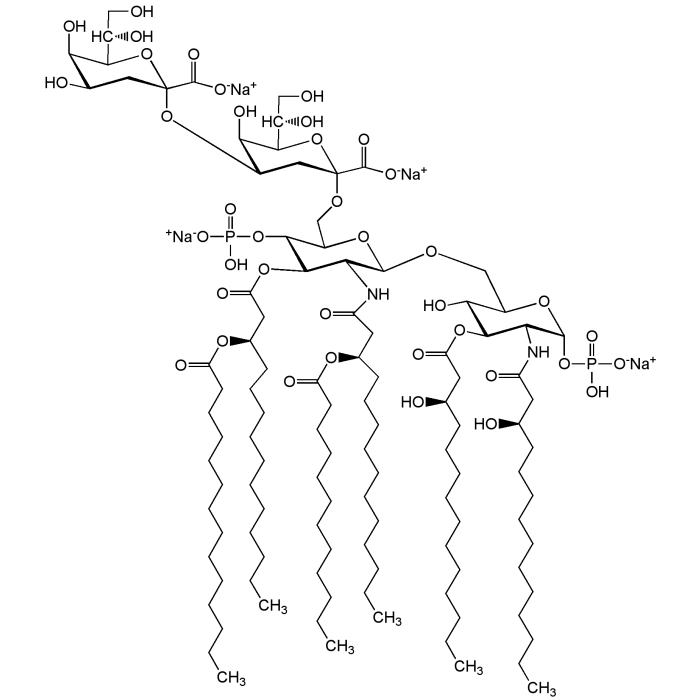
Kdo2-Lipid A (ready-to-use)
As low as
170
CHF
CHF 170.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CU1-0001-M0011 mgCHF 170.00
TLR4-dependent IL-6 production of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) induced by highly active and pure Kdo2-Lipid A (Prod. No. AG-CU1-0001). No remaining agonistic activity (IL-6) in TLR4 KO BMDM is detectable when up to 50µg/ml Kdo2-Lipid A is added.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (3-Deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid)2-Lipid A |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C110H198N2Na4O39P2 |
| MW | 2326.7 |
| CAS | 123621-04-5 (free base) |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated and purified from E. coli K12 heptose-deficient strain WBB06 (Re mutant). |
| Purity Chemicals | Absence of detectable protein or DNA contaminants with agonistic TLR activity. |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless solution. |
| Formulation | Liquid. Sterile, ready-to-use solution in pyrogen-free double distilled water. |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/ml. Vial contains 2 ml. |
| Other Product Data |
Strong activator (<10ng/ml) of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Does not activate TLR2 or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice. No further re-extraction required. Can be used for priming of the inflammasome at a concentration of 50-100ng/ml. Isolated and purified from E. coli K12 heptose-deficient strain WBB06 (Re mutant) [1] by a modification of the PCP extraction method [2,3], converted to the uniform sodium salt form [4] and dissolved in sterile pyrogen-free double distilled water.
Lit: [1] Deletion of the heptosyltransferase genes rfaC and rfaF in Escherichia coli K-12 results in a Re-type lipopolysaccharide with a high degree of 2-aminoethanol phosphate substitution: W. Brabetz, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 247, 716 (1997) / [2] A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 9, 245 (1969) / [3] Isolation and purification of R-form lipopolysaccharides: C. Galanos & O. Luderitz; Meth. Carbohydrate Chem. 9, 11 (1993) / [4] Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms: C. Galanos & O. Lüderitz; Eur. J. Biochem. 54, 603 (1975) |
| InChi Key | HBSUHPVFGADBOQ-USMMBHRMSA-N |
| Smiles | [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O[C@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)CC(=O)OC1[C@H](NC(=O)C[C@@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCC)[C@H](OCC2O[C@H](OP(O)([O-])=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C[C@H](O)CCCCCCCCCCC)C(OC(=O)C[C@H](O)CCCCCCCCCCC)[C@@H]2O)OC(CO[C@@]2(CC(O[C@@]3(CC(O)[C@@H](O)C(O3)[C@@H](O)CO)C([O-])=O)[C@@H](O)C(O2)[C@@H](O)CO)C([O-])=O)[C@H]1OP(O)([O-])=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep sterile. Do not ingest. Wear gloves and mask. Avoid contact through all modes of exposure. Avoid inhalation and prevent from entering the bloodstream. Use must be restricted to qualified personnel. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Defined substructure of the Re mutant of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [1].
- Endotoxin activity equal to Re LPS [1].
- Strong activator (<10ng/ml) of macrophages via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) [1, 2, 3, 4, 9].
- Does not activate TLR2 [5] or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice by IL-6 ELISA [1,4].
- Facilitates the structural analysis of its complexes with signaling receptors, such as TLR4/MD2 [1,2] and CD14 [7].
- Kdo2-Lipid A was used in a recent animal atherosclerosis model [6].
- Induces sphingolipid biosynthesis, which is essential for induction of autophagy [8].
Product References
- Kdo2-Lipid A of Escherichia coli, a defined endotoxin that activates macrophages via TLR-4: C.R. Raetz, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 47, 1097 (2006)
- Aggregation behavior of an ultra-pure lipopolysaccharide that stimulates TLR-4 receptors: H. Sasaki & S.H. White; Biophys. J. 95, 986 (2008)
- TLR-4 mediated group IVA phospholipase A(2) activation is phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase 1 and protein kinase C dependent: A. Grkovich, et al.; BBA 1791, 975 (2009)
- Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR 4-activated macrophages: A.Y. Andreyev, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 51, 2785(2010)
- Spinal glial TLR4-mediated nociception and production of prostaglandin E and TNF: O. Saito, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 160, 1754 (2010)
- Low doses of lipopolysaccharide and minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein cooperatively activate macrophages via nuclear factor kappab and activator protein-1- possible mechanism for acceleration of atherosclerosis by subclinical endotoxemia: P. Wiesner, et al.; Circ. Res. 107, 56 (2010)
- NMR spectral mapping of Lipid A molecular patterns affected by interaction with the innate immune receptor CD14: S. Albright, et al.; BBRC 378, 721 (2009)
- Kdo2-lipid A, a TLR4-specific agonist, induces de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in RAW264.7 macrophages, which is essential for induction of autophagy: K. Sims, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 28568 (2010)
- ATF3 plays a key role in Kdo2-lipid A-induced TLR4-dependent gene expression via NF-?B activation: E.Y. Kim, et al.; PLoS One 5, e14181 (2010)