Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
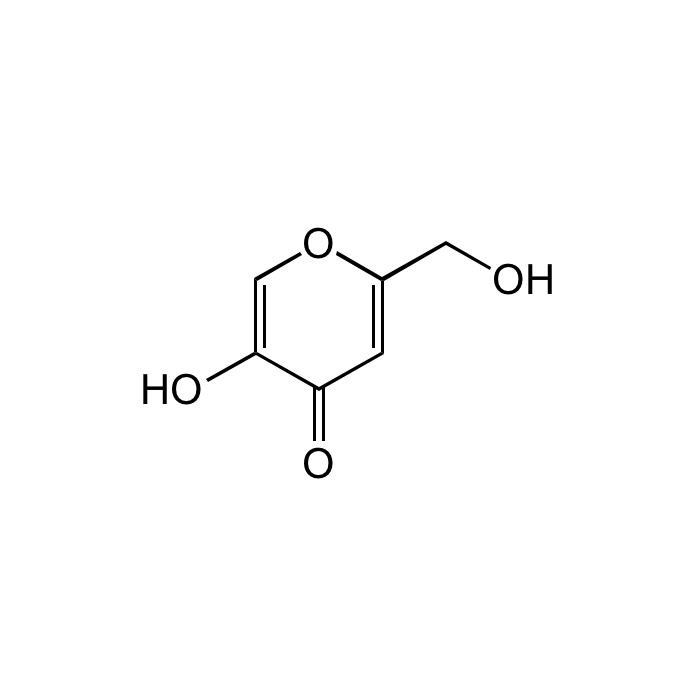
Kojic acid
As low as
55
CHF
CHF 55.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0019-M01010 mgCHF 55.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 5-Hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4H-pyran-4-one; KOJ |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C6H6O4 |
| MW | 142.1 |
| Merck Index | 14: 5317 |
| CAS | 501-30-4 |
| RTECS | UQ0875000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Aspergillus sp. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, methanol or water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| InChi Key | BEJNERDRQOWKJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OCC1=CC(=O)C(O)=CO1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Mycotoxin. Chelation agent with polyfunctional skeleton for development of biologically active compounds.
- Moderate antibacterial agent.
- Tyrosinase inhibitor. Inhibits catecholase activity of tyrosinase.
- Anti-melanogenic. Skin whitening agent.
- Antioxidant. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger.
- D-Amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitor.
- Shown to inhibit NF-kB activation.
- Inducer of macrophage activation.
- Radioprotectant activity.
- Antileishmanial agent.
- Insecticidal.
- Antifungal chemosensitizer.
- Used in cosmetics and as food additive.
Product References
- The contitution of kojic acid, a gamma-pyrone derivative of Aspergillus oryzae from carbohydrates: T. Yabuta; J. Chem. Soc. 125, 575 (1924)
- Toxicity and Antibiotic Activity of Kojic Acid Produced by Aspergillus luteo-virescens: H.E. Morton, et al.; J. Bacteriol. 50, 579 (1945)
- Kojic acid scavenges free radicals while potentiating leukocyte functions including free radical generation: Y. Niwa & H. Akamatsu; Inflammation 15, 303 (1991)
- Kojic acid, a cosmetic skin whitening agent, is a slow-binding inhibitor of catecholase activity of tyrosinase: J. Cabanes, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46, 982 (1994)
- The combination of glycolic acid and hydroquinone or kojic acid for the treatment of melasma and related conditions: A. Garcia & J.E. Fulton Jr.; Dermatol. Surg. 22, 443 (1996)
- Kojic acid--a new leading molecule for a preparation of compounds with an anti-neoplastic potential: L. Novotny, et al.; Neoplasma 46, 89 (1999) (Review)
- Kojic acid, a potential inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation in transfectant human HaCaT and SCC-13 cells: K.Y. Moon, et al.; Arch. Pharm. Res. 24, 307 (2001)
- Effects of mycotoxins, kojic acid and oxalic acid, on biological fitness of Lygus hesperus (Heteroptera: Miridae): J. Alverson; J. Invertebr. Pathol. 83, 60 (2003)
- From miso, sake and skoyu to cosmetics: a century of science for kojic acid: R. Bentley; Nat. Prod. Rep. 23, 1046 (2006) (Review)
- Kojic acid and its manganese and zinc complexes as potential radioprotective agents: S. Emami, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 45 (2007)
- Kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus sp., acts as an inducer of macrophage activation: A.P. Rodrigues, et al.; Cell Biol. Int. 35, 335 (2011)
- Synthesis of kojic acid derivatives as secondary binding site probes of D-amino acid oxidase: M. Raje, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 3910 (2013)
- Synergism of antifungal activity between mitochondrial respiration inhibitors and kojic acid: J.H. Kim, et al.; Molecules 18, 1564 (2013)
- A novel function for kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus fungi, as antileishmanial agent: A.P. Rodrigues, et al.; PLoS One 9, e91259 (2014)
- A tyrosinase inhibitor from Aspergillus niger: K.Y. Vasantha, et al.; J. Food Sci. Tech. 51, 2877 (2014)
- Application of FTIR microspectroscopy for characterization of biomolecular changes in human melanoma cells treated by sesamol and kojic acid: M. Srisayam, et al.; J. Dermatol. Sci. 73, 241 (2014)
- Feeding Deterrence, acute toxicity and sublethal growth effects of kojic acid isolated from Aspergillus funiculosus: S. Busi, et al.; Nat. Prod. J. 4, 18 (2014)