Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
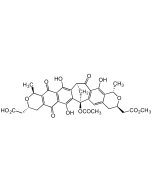
Kirromycin
As low as
215
CHF
CHF 215.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0157-M0011 mgCHF 215.00
BVT-0157-M0055 mgCHF 865.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Mocimycin; Delvomycin; MYC 8003; NSC 316094 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
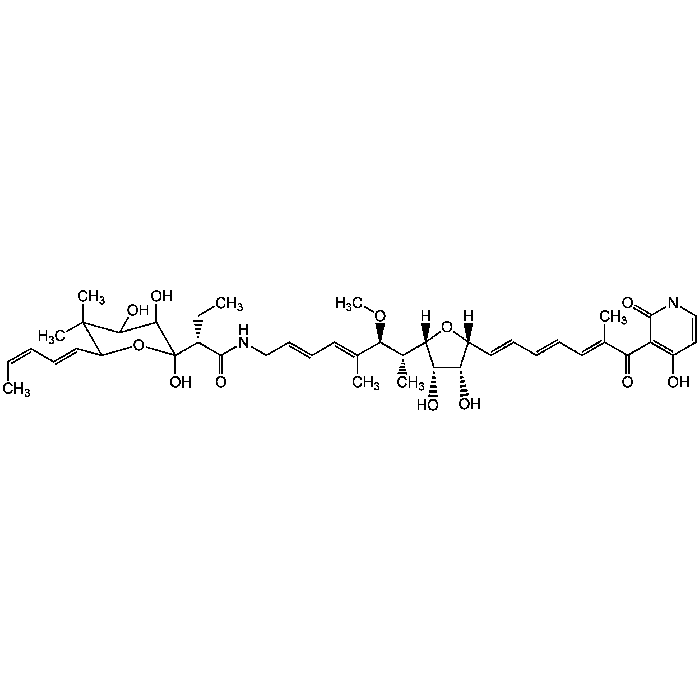
| Formula |
C43H60N2O12 |
| MW | 796.9 |
| Merck Index | 14: 6225 |
| CAS | 50935-71-2 |
| RTECS | QA2805000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces collinus. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥96% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol or DMSO. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR and UV. |
| InChi Key | HMSYAPGFKGSXAJ-PAHGNTJYSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(O[C@@]([H])([C@H](C)[C@H](OC)C(\C)=C\C=C\CNC(=O)[C@@H](CC)C2(O)OC(\C=C\C=C/C)C(C)(C)C(O)C2O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)\C=C\C=C\C=C(/C)C(=O)C1=C(O)C=CNC1=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. Store solutions at -20°C in the dark. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic. Member of the elfermycin group.
- Antibacterial.
- Protein biosynthesis inhibitor.
- Specifically interacts with the bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu and prevents the release of EF-Tu from the bacterial ribosome after GTP hydrolysis. In the absence of ribosomes it induces EF-Tu-dependent hydrolysis of GTP.
- Animal growth promoter used in poultry breeding.
Product References
- Metabolic products of microorganisms. 99. Kirromycin: H. Wolf & H. Zähner; Arch. Mikrobiol. 83, 147 (1972)
- Kirromycin, an inhibitor of the 30 S ribosomal subunits function: H. Wolf, et al.; FEBS Lett. 21, 347 (1972)
- The total structure of the novel antibiotic mocimycin: C. Vos & P.E.J. Verwiel; Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 5173 (1973)
- Kirromycin, an inhibitor of the protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu: H. Wolf, et al.; PNAS 71, 4910 (1974)
- Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes: H. Wolf, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 75, 67 (1977)
- Action of pulvomycin and kirromycin on eukaryotic cells: B. Schmid, et al.; FEBS Lett. 96, 189 (1978)
- Energetic aspects of the EF-Tu-dependent GTPase activity. A study using the antibiotic kirromycin: V. Bocchin, et al.; Eur. J. Biochem. 113, 53 (1980)
- Effects of elfamycins on elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: C.C. Hall, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33, 322 (1989)
- Inhibitory mechanisms of antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu: T. Hogg, et al.; Curr. Prot. Pept. Sci. 3, 121 (2002)
- Elongation factor Tu-targeted antibiotics: four different structures, two mechanisms of action: A. Parmeggiani & P. Nissen; FEBS Lett. 580, 4576 (2006) (Review)
- Molecular analysis of the kirromycin biosynthetic gene cluster: T. Weber, et al.; Chem. Biol. 15, 175 (2008)
- GTPase activation of elongation factor EF-Tu by the ribosome during decoding: J.-C. Schuette, et al.; EMBO J. 28, 755 (2009)
- Interaction of apicoplast-encoded elongation factor EF-Tu with nuclear-encoded EF-Ts mediates translation in the Plasmodium falciparum plastid: S. Biswas, et al.; Intern. J. Parasitol. 41, 417 (2011)
- The phosphopantetheinyl transferase kirP activates the ACP and PCP domains of the kirromycin NRPS/ PKS of Streptomyces collinus Tü 365: M. Pavlidou, et al.; FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 319, 26 (2011)