Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
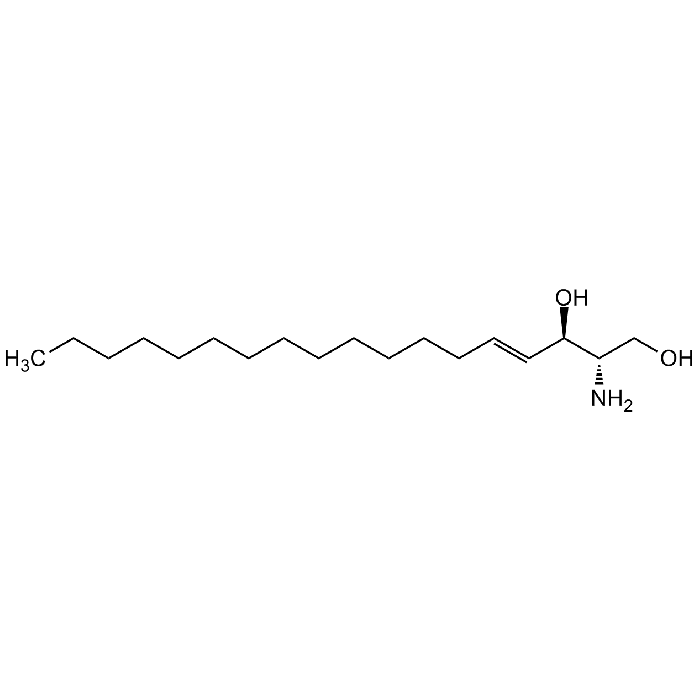
D-Sphingosine
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (2S,3R,4E)-2-Amino-4-octadecene-1,3-diol; D-erythro-Sphingosine C-18; (-)-Sphingosine |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C18H37NO2 |
| MW | 299.49 |
| CAS | 123-78-4 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥ 97% (TLC) |
| Appearance | White powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, DMSO, methanol or chloroform (10mg/ml). Insoluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 11H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | WWUZIQQURGPMPG-KRWOKUGFSA-N |
| Smiles | OC[C@@](N)([H])[C@]([H])(O)/C=C/CCCCCCCCCCCCC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
D-Sphingosine is a characteristic structural unit of many sphingolipids such as ceramides, gangliosides, globosides, sulfatides, sphingomyelin, and others. It is most abundant in nervous tissue and cell membranes. Sphingosine with an 18-carbon chain and a double bond at carbon 4 is the most abundant sphingosine in animal tissues. D-Sphingosine inhibits protein kinase C and phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase, whereas it activates phospholipase D, diacylglycerol (DAG) kinase and the cation channel TRPM3. Phosphorylation of sphingosine by sphingosine kinases 1 and 2 (SPHK 1, SPHK 2) produces sphingosine-1-phosphate, a potent bioactive lipid that exhibits a broad spectrum of biological activities including cell proliferation, survival, migration, cytoskeletal organization and morphogenesis.
(1) W.A. Khan, et al.; BBRC 172, 683 (1990) | (2) W.A. Khan, et al.; Biochem. J. 278, 387 (1991) | (3) Y.A. Hannun, et al.; Biochemistry 40, 4893 (2001) | (4) Y. Takuwa, et al.; J. Biochem. 131, 767 (2002) | (5) M.J. Kluk & T. Hla; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1582, 72 (2002) | (6) I. Ishii, et al.; Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 321 (2004) | (7) H. Nakamura, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 484, 9 (2004) | (8) C. Grimm, et al.; Mol. Pharmacol. 67, 798 (2005) | (9) V.T. Pham, et al.; Arch. Pharm. Res. 30, 22 (2007) | (10) K. Held, et al.; Temperature 2, 201 (2015)





