Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
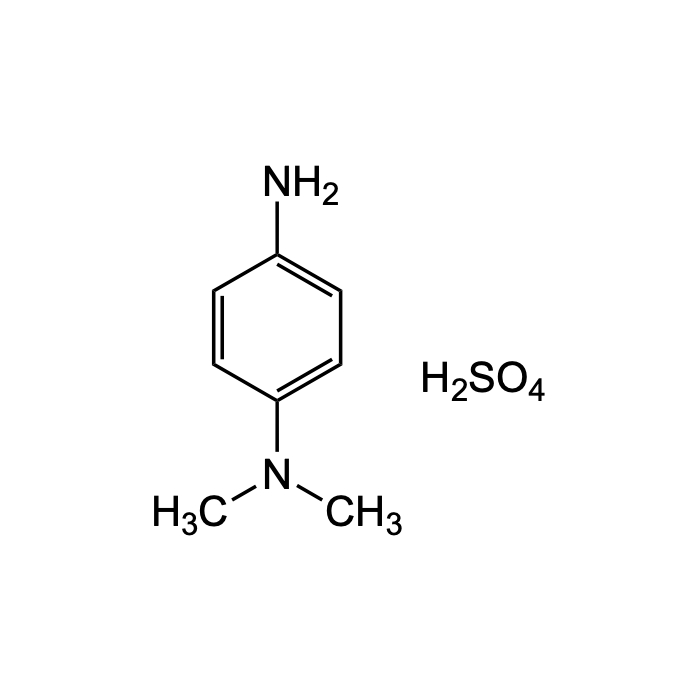
N,N-Diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate salt
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DPD sulfate; 4-Amino-N,N-diethylaniline sulfate salt; N,N-Diethyl-1,4-phenylenediammonium sulfate; Color Developing Agent 1 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C10H18N2O4S |
| MW | 262.33 |
| CAS | 6283-63-2 |
| RTECS | SS9625000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in water (100mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | AYLDJQABCMPYEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | CCN(CC)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N.OS(=O)(=O)O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
N,N-Diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate (DPD) is used as a chromogenic indicator or reagent in analytical chemistry and in water quality testing. It is commonly used in a test called the DPD method, primarily for the measurement of free and total chlorine by titrimetric, colorimetric and spectroscopic methods in water. DPD reacts with free chlorine (hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ions) to form a pink or magenta-colored compound. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the concentration of chlorine, making it a convenient method for chlorine quantification. In general, it is used for spectrophotometric determination KIO4 levels, drugs (containing phenolic groups or aromatic amino groups) and as a peroxidase substrate. DPD has been developed as a color developing agent in photgraphy.
(1) G. Gordon, et al.; Talanta 38, 145 (1991) | (2) L. Moberg & B. Karlberg; Anal. Chim. Acta 407, 127 (2000) | (3) F.H. Metwally, et al.; Farmaco 56, 601 (2001) | (4) M. Hasani, et al.; J. Hazard. Mat. 157, 161 (2008) | (5) P. Nagaraja, et al.; Acta Pharm. 60, 217 (2010) | (6) F. Yang, et al.; Mikrochim. Acta 186, 417 (2019) | (7) M. Zhou, et al.; Anal. Chem. 93, 769 (2021)





