Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
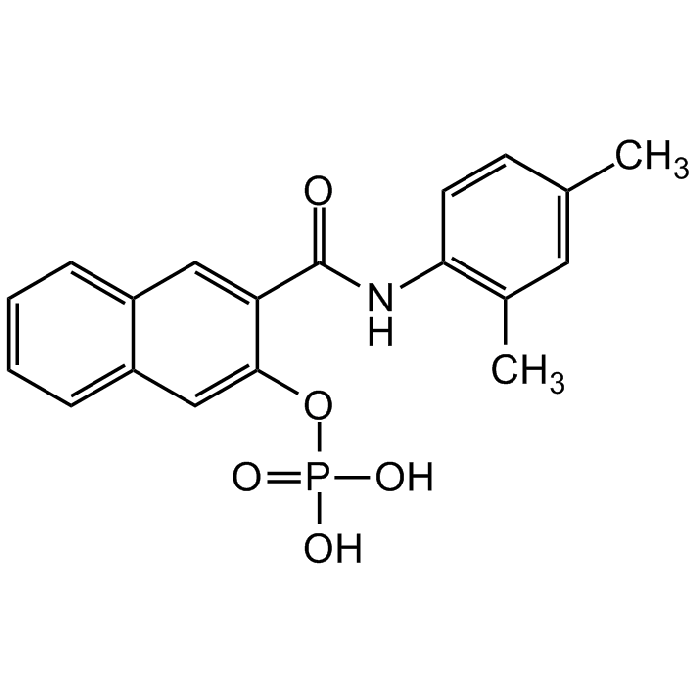
Naphthol AS-MX phosphate
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 3-[(2,4-Dimethylphenyl)carbamoyl]naphthalen-2-yl dihydrogen phosphate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C19H18NO5P |
| MW | 371.32 |
| CAS | 1596-56-1 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥99% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol (50mg/ml) or water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | IOMLBTHPCVDRHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(NC1=C(C)C=C(C)C=C1)C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C2OP(O)(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep under inert gas. Very hygroscopic. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Naphthol AS-MX Phosphate is a fluorogenic substrate for alkaline phosphatases. Naphthol AS-MX Phosphate is converted to naphthol AS-MX displaying excitation/emission spectra of 388/512nm. The fluorescence is a quantitative marker of acid and alkaline phosphatase activity. Acid and alkaline phosphatases are often used as clinical markers of disease, since the concentration of human acid and alkaline phosphatases undergo pronounced changes in particular diseases, resulting in unusually high or low concentrations. It is a histochemical substrate commonly used in conjunction with diazonium salts to form a specific azo dye for immunohistology, immunoblotting and dot blot applications.
(1) Z. Lojda, etal.; Histochemie 11, 13 (1967) | (2) G.G. Guilbault & A. Vaughan; Anal. Lett. 3, 1 (1970) | (3) A. Vaughan, et al.; Anal. Chem. 43, 721 (1971) | (4) A.S.H.De Jong, et al.; Histochem. J. 17, 1119 (1985) | (5) S. West, et al.; Anal. Biochem. 190, 254 (1990) | (6) R. Gillitzer, et al.; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38, 307 (1990) | (7) E.J. Speel, et al.; J. Histochem. Cytochem. 40, 1299 (1992) | (8) J. Espada, et al.; Histochem. Cell Biol. 108, 481 (1997)





