Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
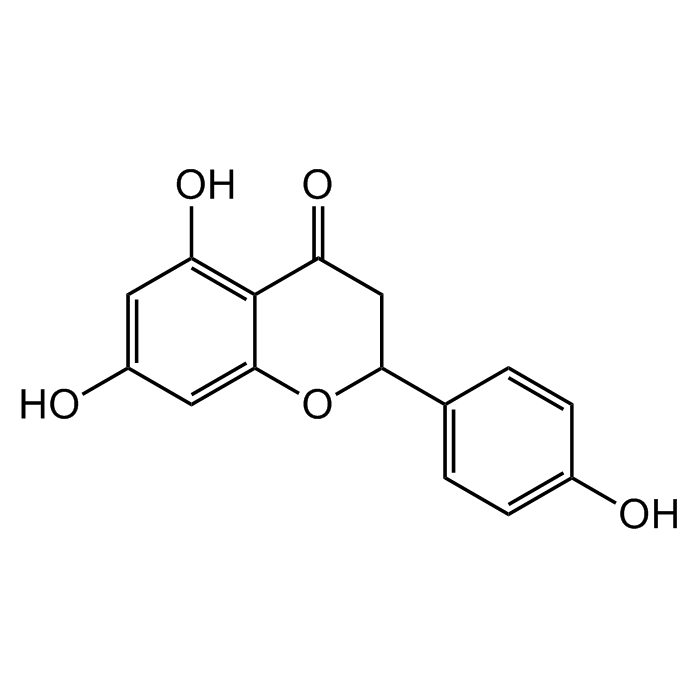
(±)-Naringenin
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | (±)-2,3-Dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one; 4',5,7-Trihydroxyflavanone; S-Dihydrogenistein; NSC 11855; NSC 34875; Salipurol |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H12O5 |
| MW | 272.25 |
| CAS | 67604-48-2 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Plant |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Off-white to beige powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (5mg/ml), DMF (10mg/ml) or ethanol (2mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | FTVWIRXFELQLPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Smiles | OC1=CC(O)=C2C(OC(C3=CC=C(O)C=C3)CC2=O)=C1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Naringenin is a citrus-derived flavonoid that inhibits CYP3A4 activity in human liver microsomes. It has a broad panel of properties, including antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, cardioprotective and neuroprotective activities. Naringenin activity is primarily attributed to its anti-inflammatory (via inhibiting recruitment of cytokines and inflammatory transcription factors) and antioxidant (via scavenging of free radicals, bolstering of endogenous antioxidant defense system and metal ion chelation) effects. Naringenin exerts its anti-diabetic effects by inhibition of gluconeogenesis through upregulations of AMPK, leading to its lipid lowering and insulin-like properties.
(1) U. Fuhr, et al.; Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 35, 431 (1993) | (2) N. Rani, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 22, 4341 (2016) (Review) | (3) N.A. Nyane, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 803, 103 (2017) (Review) | (4) N.H. Zaidun, et al.; Life Sci. 208, 111 (2018) (Review) | (5) W. Zeng, et al.; Pharmacol. Res. 135, 122 (2018) (Review) | (6) Z. Nouri, et al.; Biomolecules 9, E690 (2019) (Review)
- Anti-estrogenic and anti-aromatase activities of citrus peels major compounds in breast cancer: D.M. El-Kersh, et al.; Nature Sci. Rep. 11, 7121 (2021)





