Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
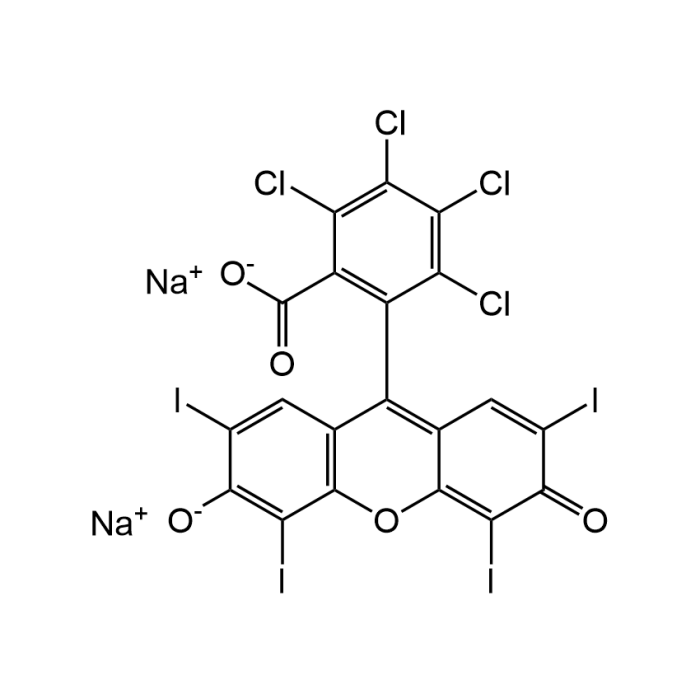
Rose Bengal sodium salt
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 4,5,6,7-Tetrachloro-2',4',5',7'-tetraiodofluorescein sodium salt; Acid Red 94; Bengal Rose B sodium salt; C.I. 45440; Sodium tetraiodotetrachlorofluorescein; Japan Red 105-1 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C20H2Cl4I4O5 . 2Na |
| MW | 1017.64 |
| CAS | 632-69-9 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Appearance | Red to brown crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml). Slightly soluble in water (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | KCQREHTWEUECQT-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Smiles | [O-]C(c1c(C2=C3C=C(C(C(I)=C3Oc4c2cc(I)c([O-])c4I)=O)I)c(Cl)c(Cl)c(Cl)c1Cl)=O.[Na+].[Na+] |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Rose Bengal is a xanthene dye, fluorescein derivative, and photosensitizer. In ophthalmology, Rose Bengal is used as a diagnostic stain to identify damaged or diseased cells in the eye. It helps in the diagnosis of dry eye syndrome and other ocular surface disorders. Rose Bengal is used in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) for treating certain types of cancers and other medical conditions. When exposed to light, Rose Bengal generates reactive oxygen species that can kill targeted cells. Rose Bengal is used to stain and differentiate various microorganisms and can be used as a tracer dye to study water movement and other environmental processes. It's spectral properties makes it useful for visual and fluorescence-based applications. Rose Bengal was originally used as a wool dye. Rose bengal inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4/5 and the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoform UGT1A6 in human liver microsomes in a light-dependent manner. Rose Bengal is a potent VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) inhibitor. High-purity form of Rose Bengal (>99.5% dye content) kills a battery of Gram-positive bacteria, including drug-resistant strains at low concentrations under fluorescent, LED, and natural light in a few minutes. Rose Bengal has been used for staining of live cells, but exhibits both intrinsic and phototoxicity. Spectral Data: λex=548nm, λem=567nm.
(1) C.W. Wu & F.Y. Wu; Biochem. 12, 4349 (1973) | (2) P.N. Marshall; Histochem. J. 8, 487 (1976) | (3) J. Paczkowski, et al.; J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1, 341 (1985) | (4) R.P. Feenstra & S.C. Tseng; Arch. Ophthalmol. 110, 984 (1992) | (5) R.P. Feenstra & S.C. Tseng; Ophthalmol. 99, 605 (1992) | (6) N. Pietrancosta, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 6922 (2010) | (7) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010) | (8) H. Kato, et al.; Photochem. Photobiol. 88, 423 (2012) | (9) M.J. Doughty; Cont. Lens Anterior Eye. 36, 272 (2013) (Review) | (10) F. Kazmi, et al.; Xenobiotica 44, 606 (2014) | (11) J. Murube; Ocul. Surf. 12, 14 (2014) | (12) B. Dhaini, et al.; Pharmaceuticals 15, 1093 (2022) (Review) | (13) M. Kurosu, et al.; Molecules 27, 322 (2022) | (14) M.H. Hakim, et al.; Bioconjug. Chem. 35, 1044 (2024)





