Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chemodex
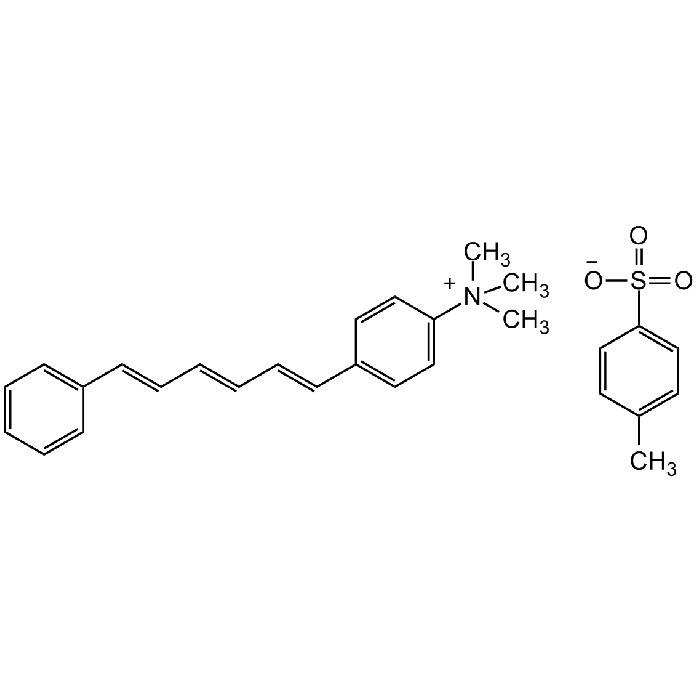
TMA-DPH
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N,N,N-Trimethyl-4-(6-phenyl-1,3,5-hexatrien-1-yl)phenylammonium p-toluenesulfonate; 1,6-Diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene-4'-trimethylammonium tosylate; 1-(4-Trimethylammoniophenyl)-6-phenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene p-toluenesulfonate |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula | C21H24N . C7H7O3S |
| MW | 461.62 |
| CAS | 115534-33-3 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥96% (TLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow, dark yellow to beige powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or methanol (1mg/ml). |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chemodex. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| InChi Key | ZKARERKEBVSZCX-VMDDUYISSA-M |
| Smiles | C[N+](C)(C)C(C=C1)=CC=C1/C=C/C=C/C=C/C2=CC=CC=C2.CC3=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C3 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
TMA-DPH is a fluorescent probe for membrane fluidity measurements in artificial and living membrane systems. Acts as an anchor at the lipid/water interface. Specifically and rapidly incorporating into the plasma membrane and between the membranes and the buffer. It is especially useful in the study of monolayer dynamics of lipoproteins and similar analogous systems, exocytosis kinetics and similar systems. TMA-DPH is cylinder-shaped and has fluorescence emission transition dipoles that are basically aligned parallel to its long molecular axis. As such, it is very sensitive to reorientation resulting from interactions with surrounding lipids. TMA-DPH is widely used in fluorescence polarization studies of rotational motion. Spectral Data: λex 355 nm; λem ~430 nm in methanol or DMSO.
(1) D. Illinger, et al.; Cell Biophys. 14, 17 (1989) | (2) C. Maire, et al.; Biorheology 29, 507 (1992) | (3) G. Ferretti, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1147, 245 (1993) | (4) D. Illinger, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 125, 783 (1994) | (5) D. Illinger, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1239, 58 (1995) | (6) J. Matko & P. Nagy; J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 40, 120 (1997) | (7) C. Saldana, et al.; J. Membr. Biol. 190, 75 (2002) | (8) B. Chazotte; Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. (2011) | (9) A.M.T.M. do Canto, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1858, 2647 (2016)





