Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
Chimerigen
IL-2 (human) (rec.) (untagged)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Interleukin-2; Aldesleukin |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | E. coli |
| Sequence |
The extracellular domain of human IL-2 (aa 21-153) with a N-terminal Met. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Biological Activity |
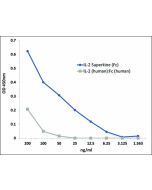
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using CTLL2 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.35-1.4ng/ml. |
| MW | ~14kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Endotoxin Content | <0.01EU/μg protein (LAL test; Lonza). |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute 10µg vial with 100 µl sterile water to a concentration of 0.1mg/ml. Reconstitute 50µg vial with 100 µl sterile water to a concentration of 0.5mg/ml. Further dilute in other aqueous solutions. |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 0.1% TFA, 70% acetonitrile. |
| Other Product Data |
NCBI reference NP_000577.2: IL-2 (human) |
| Declaration | Manufactured by Chimerigen. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -80°C |
| Handling Advice |
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Centrifuge lyophilized vial before opening and reconstitution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -80°C. Working aliquots are stable for up to 3 months when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a 133 amino acid glycoprotein with one intramolecular disulfide bond and variable glycosylation. It is secreted by activated T cells and induces proliferation and maturation of activated T cells, natural killer cells, and lymphokine activated killer cells. IL-2 also stimulates proliferation of antibody-producing B cells, activates neutrophils, and induces mononuclear cells to secrete IFN-γ and TNF-α and -β. Moreover, studies have shown that IL-2 is required for activation-induced apoptosis, an important hemeostatic mechanism in the immune system, which is involved in the maintenance of peripheral tolerance to self-antigens.