Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
RevMab
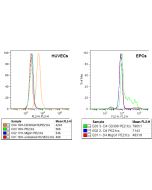
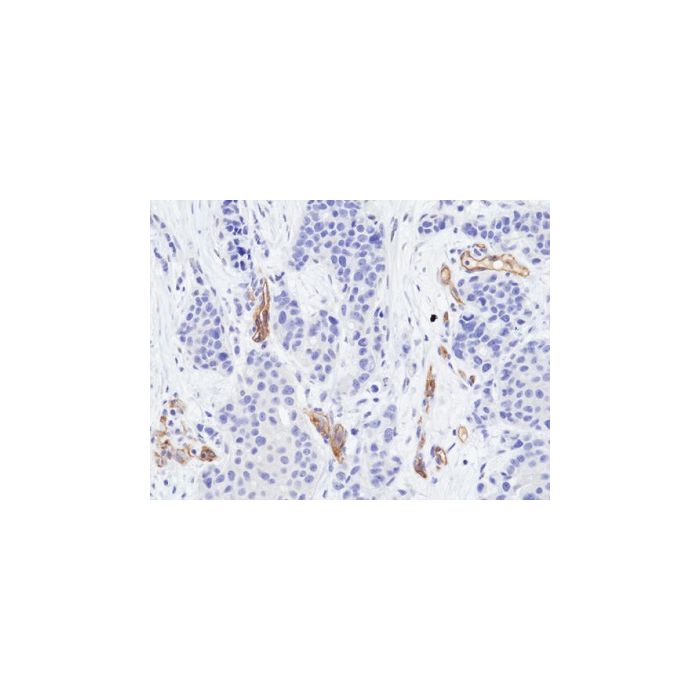
anti-VEGFR2 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM515)
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2; Kinase Insert Domain Receptor; Protein-tyrosine Kinase Receptor Flk-1; CD309; KDR; FLK-1 |
| Product Type | Recombinant Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | RM515 |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Source/Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen/Antigen | A peptide corresponding to residues near the C-terminus of human VEGFR2. |
| Application |
Immunohistochemistry (IHC): 1:100-1:200 |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
| Specificity |
This antibody reacts to human VEGFR2 (KDR; FLK-1; CD309). |
| Purity | Protein A purified. |
| Purity Detail | Protein A affinity purified from an animal origin-free culture supernatant. |
| Formulation | Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. |
| Isotype Negative Control | |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for Original Manufacturer Product Datasheet |
| Accession Number | P35968 |
| Declaration | Manufactured by RevMab Biosciences. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Disruption of the precise balance of positive and negative molecular regulators of blood and lymphatic vessel growth can lead to myriad diseases. Although dozens of natural inhibitors of hemangiogenesis have been identified, an endogenous selective inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth has not been previously described. A splice variant of the gene encoding vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) that encodes a secreted form of the protein, designated endogenous soluble VEGFR-2 (esVEGFR-2/KDR) has been described. The endogenous soluble esKDR inhibits developmental and reparative lymphangiogenesis by blocking VEGF-C function. Tissue-specific loss of esKDR in mice induced, at birth, spontaneous lymphatic invasion of the normally alymphatic cornea and hyperplasia of skin lymphatics without affecting blood vasculature. Administration of esKDR inhibited lymphangiogenesis but not hemangiogenesis induced by corneal suture injury or transplantation, enhanced corneal allograft survival and suppressed lymphangioma cellular proliferation. Naturally occurring esKDR thus acts as a molecular uncoupler of blood and lymphatic vessels; modulation of esKDR might have therapeutic effects in treating lymphatic vascular malformations, transplantation rejection and, potentially, tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphedema.