Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
SouthBayBio
Ubiquitin (human) (rec.) (6-FAM)
As low as
291
CHF
CHF 291.00
In stock
Only %1 left
SBB-TR0016-C05050 µgCHF 291.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | UBB; Ubiquitin B |
| Product Type | Protein |
| Properties | |
| Source/Host | E. coli |
| Sequence | Human ubiquitin (aa1-76) (Accession Nr. P0CG47) is site-specifically conjugated to a single fluorescein (6-FAM) moiety. All lysines are available along with a fully functional C-terminus, making it ideal for chain formation using the E1-E2 and E3 conjugation cascade. |
| Crossreactivity | Human |
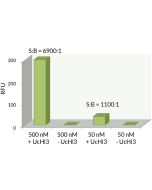
| Application | Protein-Based TR-FRET Pair Acceptor. Typical working concentration range is 250nM-500nM. Best working concentration needs to be empirically determined by the type of application by the end user. 6-FAM-Ub has an excitation maximum of 494nm and an emission maximum of 520nm. |
| Label/Conjugates | 6-FAM |
| MW | ~9kDa |
| Purity | ≥98% (LCMS) |
| Concentration | Lot dependent. |
| Accession Number | P0CG47 |
| Formulation | Liquid. In 50mM HEPES pH 7.5, 50mM sodium chloride. |
| Other Product Data |
Click here for a Typical Lot-specific Product Datasheet from the Original Manufacturer Our product description may differ slightly from the original manufacturers product datasheet. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by South Bay Bio. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | DRY ICE |
| Short Term Storage | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage | -80°C |
| Handling Advice |
Aliquot to avoid freeze/thaw cycles. Protect from light. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -80°C. |
| Documents | |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Ubiquitin is a highly conserved protein that plays a major role in the ubiquitination pathway, which is conserved from yeast to mammals. Ubiquitination, the conjugation of ubiquitin to other proteins through a covalent bond between its C-terminal glycine and the ε-amino group of lysine residues or the α-amino group of an N- terminal methionine onto proteins is essential for many cellular processes primarily linked to protein degradation. This process involves three steps with specific groups of enzymes in an ATP depended manner, which are activation with ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), conjugation with ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) and ligation with ubiquitin ligases (E3s).