Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
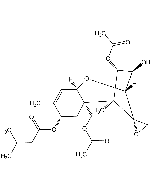
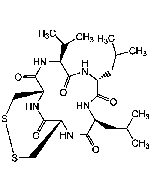
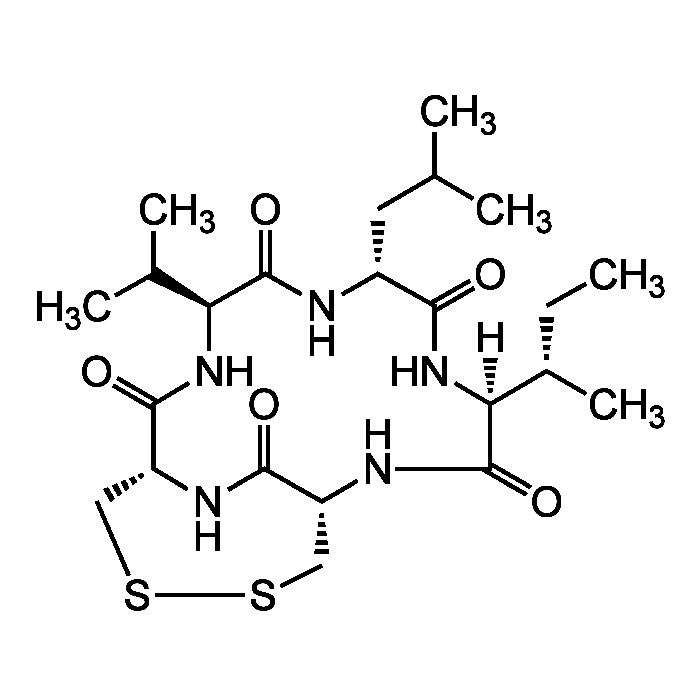
Malformin A1
As low as
130
CHF
CHF 130.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0169-C250250 µgCHF 130.00
AG-CN2-0169-M0011 mgCHF 390.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Malformin A; Cyclic(D-cysteinyl-D-cysteinyl-L-valyl-D-leucyl-L-isoleucyl)cyclic(1-2)-disulfide |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C23H39N5O5S2 |
| MW | 529.7 |
| CAS | 3022-92-2 |
| RTECS | ON7050000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from Aspergillus niger. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO. |
| InChi Key | BEZOVOWRERTMCU-VEXWFWOFSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@]1(NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H]2CSSC[C@@H](NC1=O)C(=O)N2)C(C)C)[C@@H](C)CC |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Keep cool and dry. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Peptide antibiotic. Antibcaterial [1].
- Plant growth stimulator [2].
- Induces root curvature and malformation in plants [3].
- Mycotoxin [4].
- Prevents interleukin-1 (IL-1) induced endothelial changes by inhibition of protein synthesis [5].
- Inhibitor of interleukin-1 β (IL1 β) binding to its receptor [6].
- Enhancer of cellular fibrinolytic activity [7, 12].
- Disrupts the cell cycle at the G2 checkpoint of cancer cells, leading to sensitization of the cancer cells to anti-cancer reagents [8].
- Anticancer compound. Cytotoxic against several cancer cell lines [9].
- Antimalarial and antitrypanosomal [10].
- Inhibitor of BRAF-mutated melanoma cell lines [11].
Product References
- Antibiotic properties of malformin: S. Suda & R.W. Curtis; Appl. Microbiol. 14, 475 (1966)
- Stimulation of plant growth by malformin A: W.W. John & R.W. Curtis; Experientia 30, 1392 (1974)
- Structure and synthesis of malformin A1: M. Bodanszky & G.L. Stahl; Bioorg. Chem. 4, 93 (1975)
- Mycotoxins from mold fungi-weapons of uninvited fellow-boarders of man and animal: structures, biological activity, biosynthesis, and precautions: B. Franck; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 23, 493 (1984)
- Malformin A prevents IL-1 induced endothelial changes by inhibition of protein synthesis: P.G. Bannon, et al. Thromb. Haemost. 72, 482 (1994)
- Malformin-A1 inhibits the binding of interleukin-1 beta (IL1 beta) and suppresses the expression of tissue factor in human endothelial cells and monocytes: J.M. Herbert, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 1211 (1994)
- Enhancement of fibrinolytic activity of U937 cells by malformin A1: Y. Koizumi & K. Hasumi; J. Antibiot. 55, 78 (2002)
- Fungal malformins inhibit bleomycin-induced G2 checkpoint in Jurkat cells: K. Hagimori, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 30, 1379 (2007)
- Asperpyrone D and other metabolites of the plant-associated fungal strain Aspergillus tubingensis. J. Zhan, et al.; Phytochem. 68, 368 (2007)
- Solid-phase synthesis and biological activity of malformin C and its derivatives: Y. Kojima, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 62, 681 (2009)
- A cell-based screening to detect inhibitors of BRAF signaling pathway: Y. Asami, et al.; J. Antibiot. 62, 105 (2009)
- Fibrinolytic activation promoted by the cyclopentapeptide malformin: involvement of cytoskeletal reorganization: Y. Koizumi, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34, 1426 (2011)
- Malformin A1 treatment alters invasive and oncogenic phenotypes of human colorectal cancer cells through stimulation of the p38 signaling pathway: SY. Park, et al.; Int. J. Oncol. 51, 959 (2017)