Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
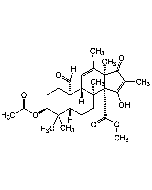
Ophiobolin A
As low as
150
CHF
CHF 150.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0431-C100100 µgCHF 150.00
AG-CN2-0431-M0011 mgCHF 450.00

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Cochliobolin A; Ophiobalin; NSC 114340 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C25H36O4 |
| MW | 400.6 |
| CAS | 4611-05-6 |
| RTECS | RL1576000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Bipolaris leersia. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMSO or dimethylformamide. Poorly soluble in water. |
| InChi Key | MWYYLZRWWNBROW-BDZRSQQBSA-N |
| Smiles | [H]C(=O)C1=C[C@]2([H])[C@](C)(CC[C@@]22O[C@H](C[C@@H]2C)C=C(C)C)C[C@@]2([H])[C@]1([H])C(=O)C[C@@]2(C)O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Keep under inert gas. Protect from light. Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cell permeable, irreversible calmodulin antagonist. Acts by covalently binding to a lysine-rich inhibitory site. Inhibits by blocking the activation of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase [1-3, 5, 6, 9].
- Herbicidal mycotoxin [7].
- Phytotoxic, antifungal, antibacterial and nematocidal compound [4, 6, 10].
- Anticancer compound. Shown to induce paraptosis-like cell death [11, 12].
- Shown to inhibit P-glycoprotein-mediated transport [8].
- Disruptor of intracellular sulfhydryl proteostasis, leading to ER stress and dilation.
Product References
- Ophiobolin A. A natural product inhibitor of calmodulin: P.C. Leung, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 259, 2742 (1984)
- Role of Calmodulin Inhibition in the Mode of Action of Ophiobolin A: P.C. Leung, et al.; Plant Physiol. 77, 303 (1985)
- Characterization of the interaction of ophiobolin A and calmodulin: P.C. Leung, et al.; Int. J. Biochem. 20, 1351 (1988)
- Microbial metabolites of ophiobolin A and antimicrobial evaluation of ophiobolins: E. Li, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 58, 74 (1995)
- Identification of the binding and inhibition sites in the calmodulin molecule for ophiobolin A by site-directed mutagenesis: T. Kong Au & P. Chow Leung; Plant Physiol. 118, 965 (1998)
- The biology of ophiobolins: T.K. Au, et al.; Life Sci. 67, 733 (2000) (Review)
- Herbicidal potential of ophiobolins produced by Drechslera gigantea: A. Evidente, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 1779 (2006)
- Inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport by terpenoids contained in herbal medicines and natural products: N. Yoshida, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 44, 2033 (2006)
- Calcium depletion and calmodulin inhibition affect the import of nuclear-encoded proteins into plant mitochondria: S. Kuhn, et al.; Plant J. 58, 694 (2009)
- Effect of the sesterterpene-type metabolites, ophiobolins A and B, on zygomycetes fungi: K. Krizsan, et al.; FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 313, 135 (2010)
- Ophiobolin A induces paraptosis-like cell death in human glioblastoma cells by decreasing BKCa channel activity: M. Bury, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 4, e561 (2013)
- Ophiobolin A, a sesterterpenoid fungal phytotoxin, displays higher in vitro growth-inhibitory effects in mammalian than in plant cells and displays in vivo antitumor activity: M. Bury, et al.; Int. J. Oncol. 43, 575 (2013)
- Ophiobolin A kills human glioblastoma cells by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress via disruption of thiol proteostasis: I.Y. Kim, et al.; Oncotarget 8, 106740 (2017)