Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
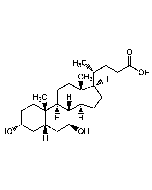
Chenodeoxycholic acid
As low as
25
CHF
CHF 25.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0410-M100100 mgCHF 25.00
AG-CN2-0410-M500500 mgCHF 90.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CDCA; Ulmenide; Kebilis; Hekbilin; Fluibil; Chenodiol; Anthropodeoxycholic acid |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C24H40O4 |
| MW | 392.6 |
| Merck Index | 14: 2054 |
| CAS | 474-25-9 |
| RTECS | FZ1980000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. Originally isolated from bile. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by IR |
| InChi Key | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-BSWAIDMHSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice |
Protect from light. Protect from moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Cytotoxic hydrophobic primary bile acid [1].
- Activator of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that is hepatoprotective and regulates bile acid synthesis (cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) suppression), conjugation and transport, as well as genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and [4-6, 14].
- Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis [1, 8, 9, 12].
- Inhibitor of 5β-reductase (AKR1D1) [10, 15].
- Potent selective inhibitor of DD2 (AKR1C2) [3].
- Potent inhibitor of 11β-HSD1 dehydrogenase [7].
- Changes tumor cell viability via IL-6 pathway [11].
- Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer [13].
- Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory compound. Modulates oxidative stress [2, 16].
- Differentiation regulator of mouse embryonic stem cells [17].
- Used for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones.
Product References
- Bile acids as drugs: principles, mechanisms of action and formulations: A.F. Hofmann; Ital. J. Gastroenterol. 27, 106 (1995) (Review)
- S-adenosil-L-methionine is able to reverse the immunosuppressive effects of chenodeoxycholic acid in vitro: G. Filaci, et al.; Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 19, 157 (1997)
- Identification of amino acid residues responsible for differences in substrate specificity and inhibitor sensitivity between two human liver dihydrodiol dehydrogenase isoenzymes by site-directed mutagenesis: K. Matsuura, et al.; Biochem. J. 323, 61 (1997)
- Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids: M. Makishima, et al.; Science 284, 1362 (1999)
- Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor: D.J. Parks, et al.; Science 284, 1365 (1999) (Review)
- A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an anatagonist ligand for FXR: N.L. Urizar, et al.; Science 296, 1703 (2002)
- Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in various target tissues: D.J. Morris, et al.; Metabolism 53, 811 (2004)
- The Farnesoid X Receptor - A Molecular Link Between Bile Acid and Lipid and Glucose Metabolism: T. Claudel, et al.; Hepatology 48, 1632 (2008) (Review)
- Farnesoid X receptor antagonizes nuclear factor kappaB in hepatic inflammatory response: Y.D. Wang, et al.; Hepatology 48, 1632 (2008) (Review)
- Bile acids modulate glucocorticoid metabolism and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in obstructive jaundice: A.D. McNeilly, et al.; J. Hepatol. 52, 705 (2010)
- Effects of bile acids on expression of interleukin-6 and cell viability in QBC939 cell line: J. Wang, et al.; Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 48, 919 (2010)
- Fasting plasma chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid concentrations are inversely correlated with insulin sensitivity in adults: B. Cariou, et al.; Nutrition & Metabolism 8, 48 (2011)
- Deoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic bile acids induce apoptosis via oxidative stress in human colon adenocarcinoma cells: J.I. Barrasa, et al.; Apoptosis 16, 1054 (2011)
- Farnesoid X receptor activation by chenodeoxycholic acid induces detoxifying enzymes through AMP-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated phosphorylation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β: K. Noh, et al.; Drug Metab. Dispos. 39, 1451 (2011)
- Substrate specificity and inhibitor analyses of human steroid 5β-reductase (AKR1D1): M. Chen, et al.; Steroids 76, 484 (2011)
- Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on fibrosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in kidney in high-fructose-fed Wistar rats: Z. Hu, et al.; Kidney Blood Press Res. 36, 85 (2012)
- Direct effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells cultured under feeder-free culture conditions: S.J. Park, et al.; Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 375076 (2013)