Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
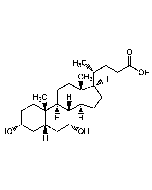
Ursodeoxycholic acid
As low as
52
CHF
CHF 52.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CN2-0411-G0011 gCHF 52.00
AG-CN2-0411-G0055 gCHF 156.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | UDCA; USAN; BRN 3219888; NSC 657950; NSC 683769 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C24H40O4 |
| MW | 392.6 |
| Merck Index | 14: 9889 |
| CAS | 128-13-2 |
| RTECS | FZ2000000 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥95% (NMR) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| InChi Key | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-UZVSRGJWSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice |
Protect from light. Protect from moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Endogenous hydrophilic bile acid.
- Antioxidant. Cytoprotective against oxidative stress and cell death.
- Hepatoprotective at cellular and molecular level, including stabilization of membranes. Protects hepatocytes against bile acid-induced apoptosis.
- Antiapoptotic and antinecrotic. Targets the mitochondrial function and integrity, reduction of endoplasmatic stress and interactions with survival signals in cAMP, Akt, NF-κB, MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways.
- Modulator and finetuner of the p53-Mdm-2 complex.
- Chemopreventive against colorectal cancer by countering the tumor-promoting effects of secondary bile acids. Shows also effects on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and COX-2 expression.
- Immunomodulator and anti-inflammatory compound. Modifies TLR4 and TLR9 signaling pathways and downregulates the production of proinflammatory tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).
- Pregnane X receptor agonist.
- Neuroprotective. Inhibits neuronal apoptosis.
- Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) agonist.
- Anticholestatic agent. Used to reduce cholesterol absorption and for cholesterol gallstone dissolution.
- Used to treat primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC).
- Interferes with the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/NASH.
- Reduces CXCR3 expression [11].
- TIMP-1 inducer [12].
- ADAM17 inhibitor [12].
- Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 virus protein synthesis.
Product References
- Antioxidant properties of ursodeoxycholic acid: D. Lapenna, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 64, 1661 (2002) (Review)
- Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited: G. Paumgartner, et al.; Hepatology 36, 525 (2002) (Review)
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an overview of current insights in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatmen. T.C. Schreuder, et al.; World J. Gastroenterol. 14, 2474 (2008) (Review)
- p53 and the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis: implications for disease pathogenesis: J.D. Amaral, et al.; Trends Mol. Med. 15, 531 (2009) (Review)
- Bile acids: regulation of apoptosis by ursodeoxycholic acid: J.D. Amaral, et al.; J. Lipid. Res. 50, 1721 (2009) (Review)
- Bile acids as regulators of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism: M. Trauner, et al.; Dig. Dis. 28, 220 (2010) (Review)
- Targeting the p53 pathway of apoptosis: J.D. Amaral, et al.; Curr. Pharm. Des. 16, 2493 (2010) (Review)
- Ursodeoxycholic acid and chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: L. Serfaty, et al.; Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 34, 516 (2010) (Review)
- Ursodeoxycholic acid and bile-acid mimetics as therapeutic agents for cholestatic liver diseases: an overview of their mechanisms of action: R. Poupon; Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 36, S3 (2012) (Review)
- Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: linking action mechanisms to therapeutic applications: M.G. Roma, et al.; Clin. Sci. (Lond). 121, 523 (2011) (Review)
- CXCR3 axis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible novel mechanism of the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid: P. Manousou, et al.; Clin. Exp. Immunol. 172, 9 (2013)
- Liver protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid includes regulation of ADAM17 activity: H. Buryova, et al.; BMC Gastroenterol. 13, 155 (2013)
- High body temperature increases gut microbiota-dependent host resistance to influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection: M. Nagai, et al.; Nature Commun. 14, 3863 (2023)