Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
AdipoGen Life Sciences
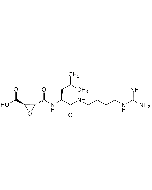
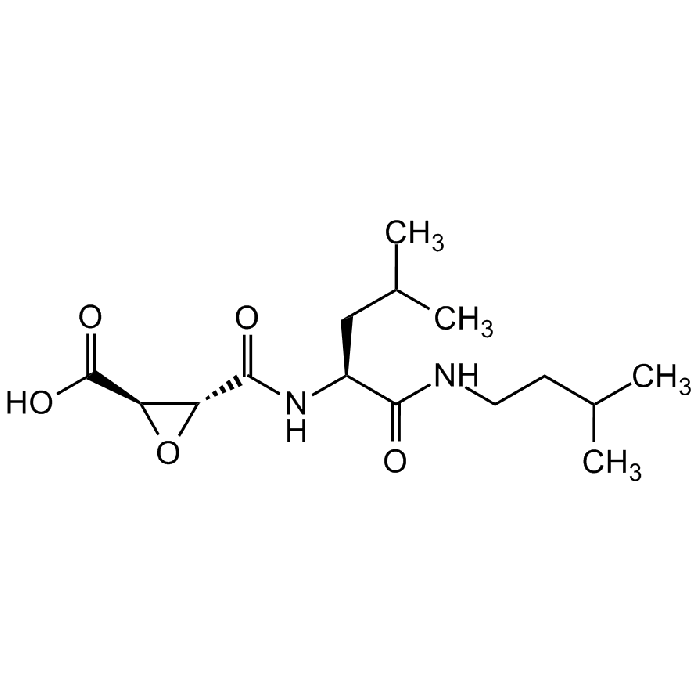
Loxistatin acid [E-64c]
As low as
70
CHF
CHF 70.00
In stock
Only %1 left
AG-CP3-7007-M0011 mgCHF 70.00
AG-CP3-7007-M0055 mgCHF 280.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Ep 475; 2S,3S-trans-(Carboxyoxirane-2-carbonyl)-L-leucine-(3-methylbutyl) amide; NSC 694279 |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C15H26N2O5 |
| MW | 314.4 |
| CAS | 76684-89-4 |
| RTECS | RR0404200 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Synthetic. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White solid. |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or ethanol (10mg/ml). Slightly soluble in water (1mg/ml). |
| InChi Key | SCMSYZJDIQPSDI-QJPTWQEYSA-N |
| Smiles | O=C(O)[C@H]1[C@H](C(N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(NCCC(C)C)=O)=O)O1 |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light and moisture. |
| Use/Stability | Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- E-64c is a potent cell-impermeable epoxysuccinyl peptide inhibitor of calpain and other cysteine proteases, such as papain, cathepsin B, H and L. Does not inhibit the serine proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin or elastase.
- E-64c is an active metabolite of the protease inhibitor E-64d (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3737), and a synthetic analog of E-64 (Prod. No. AG-CP3-7006). Studies indicate that E-64c is a more potent inhibitor of cathepsins B and L compared to E-64.
- E-64c has in vitro antiviral, antiparasitic and immunomodulatory properties. It reduces the autocatalytic activity of the foot-and-mouth-disease virus (FMDV) leader protease, reduces infection of HEK293T cells by an HIV-based virus system pseudotyped with SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein in a concentration-dependent manner, inhibits human rotavirus replication, and exhibits entry-blocking effects against MERS-CoV. It also inhibits the trypanosomal cysteine protease cruzain. Significantly reduces calpain-mediated depletion of microtubule-associated protein (MAP2) in an animal model of an ischemic brain.
Product References
- The effect of an in vivo-injected thiol protease inhibitor, E-64-c, on the calcium-induced degeneration of myofilaments: S. Ishiura, et al.; J. Biochem. 90, 1557 (1981)
- L-trans-Epoxysuccinyl-leucylamido(4-guanidino)butane (E-64) and its analogues as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases including cathepsins B, H and L: A.J. Barrett, et al.; Biochem. J. 201, 189 (1982)
- In vitro and in vivo inhibition of cysteine proteinases by EST, a new analog of E-64: M. Tamai, et al.; J. Pharmacobiodyn. 9, 672 (1986)
- Mode of binding of E-64-c, a potent thiol protease inhibitor, to papain as determined by X-ray crystal analysis of the complex: K. Matsumoto, et al.; FEBS Lett. 245, 177 (1989)
- Calcium-activated neutral protease inhibitor (E-64c) and reperfusion for experimental myocardial infarction: G. Toda, et al.; Jpn. Heart J. 30, 375 (1989)
- Protease inhibitors prevent the development of human rotavirus-induced diarrhea in suckling mice: T. Ebina & K. Tsukada; Microbiol. Immunol. 35, 583 (1991)
- Antiviral effects of a thiol protease inhibitor on foot-and-mouth disease virus: L.G. Kleina & M.J. Grubman; J. Virol. 66, 7168 (1992)
- Structural basis of inhibition of cysteine proteases by E-64 and its derivatives: K. Matsumoto, et al.; Pept. Sci. 51, 99 (1999)
- Design, synthesis and evaluation of d-homophenylalanyl epoxysuccinate inhibitors of the trypanosomal cysteine protease cruzain: W.R. Roush, et al.; Tetrahedron 56, 9747 (2000)
- Inhibitors of cathepsin L prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry: G. Simmons, et al.; PNAS 102, 11876 (2005)
- Safe, High-Throughput Screening of Natural Compounds of MERS-CoV Entry Inhibitors Using a Pseudovirus Expressing MERS-CoV Spike Protein: J.Y. Kim, et al.; Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 52, 730 (2018)






![Aloxistatin [E-64d]](https://update.adipogen.com/media/catalog/product/cache/9c281c7ec96bf9060309dac73f492a03/a/g/ag-cr1-3737.png)