Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
BioViotica
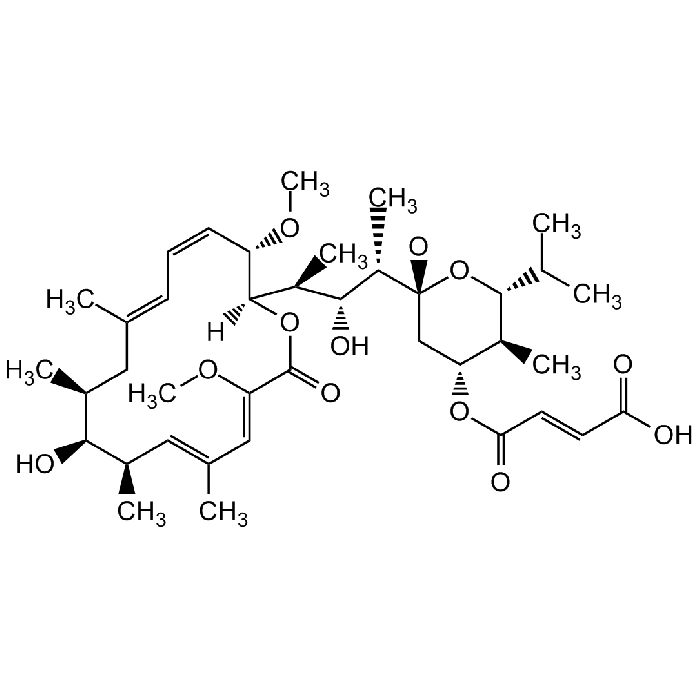
Bafilomycin C1
As low as
180
CHF
CHF 180.00
In stock
Only %1 left
BVT-0068-M0011 mgCHF 180.00
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | L-681,110A1; 2-Demethyl-2-methoxy-24-methyl-hygrolidin |
| Product Type | Chemical |
| Properties | |
| Formula |
C39H60O12 |
| MW | 720.9 |
| CAS | 88979-61-7 |
| Source/Host Chemicals | Isolated from Streptomyces sp. Gö 14F. |
| Purity Chemicals | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder. |
| Solubility | Soluble in 100% ethanol, methanol, DMSO or dimethyl formamide. |
| Identity | Determined by 1H-NMR. |
| Declaration | Manufactured by BioViotica. |
| Other Product Data |
May undergo transformation to methyl ketal on long term storage in methanol. We recommend the use of fresh solutions. |
| InChi Key | WUDBXVQNMOTFEE-WSNZTHDZSA-N |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]1(OC(=O)\C(OC)=C\C(\C)=C\[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)C\C(C)=C\C=C/[C@@H]1OC)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@@]1(O)C[C@@H](OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O)[C@H](C)[C@H](O1)C(C)C |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | -20°C |
| Handling Advice | Protect from light when in solution. |
| Use/Stability |
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C. |
| Documents | |
| MSDS |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
- Antibiotic.
- Specific vacuolar-type H+-ATPase inhibitor.
- Inhibitor of autophagic degradation by rising lysosomal pH and thus inactivating the lysosomal acid hydrolases.
- Antibacterial, insecticidal and anthelmintic.
- Antifungal activity, especially against C. albicans.
- Potential anti-osteoporotic agent in treating bone lytic diseases.
- Neuroprotection inducer.
- Cytotoxic activity against SMMC7721 HCC cells.
- Potential candidate for hepatic carcinoma chemotherapy.
Product References
- Metabolic products of microorganisms. 224. Bafilomycins, a new group of macrolide antibiotics. Production, isolation, chemical structure and biological activity: G. Werner, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 37, 110 (1984)
- Purification of vacuolar ATPase with bafilomycin C1 affinity chromatography: T.J. Rautiala, et al.; BBRC 194, 50 (1993)
- Bafilolides, potent inhibitors of the motility and development of the free-living stages of parasitic nematodes: E. Lacey, et al.; Int. J. Parasitol. 25, 349 (1995)
- Autophagy, bafilomycin and cell death: the "a-B-cs" of plecomacrolide-induced neuroprotection: J.J. Shacka, et al.; Autophagy 2, 228 (2006) (Review)
- Structure and function of V-ATPases in osteoclasts: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of osteolysis: J. Xu, et al.; Histol. Histopathol. 222, 443 (2007)
- Low-dose Bafilomycin attenuates neuronal cell death associated with autophagy-lysosome pathway dysfunction: V. Pivtoraiko, et. al.; J. Neurochem. 114, 1193 (2010)
- Alterations in osteoclast function and phenotype induced by different inhibitors of bone resorption-implications for osteoclast quality: A. Neutzsky-Wulff, et. al.; BMC Musculoskel. Disord. 11, 1471 (2010)
- Bafilomycins and Odoriferous Sesquiterpenoids from Streptomyces albolongus Isolated from Elephas maximus Feces: N. Ding, et al.; J. Nat. Prod., 79, 799 (2016)
- Bafilomycin C1 exert antifungal effect through disturbing sterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans: H. Su, et al.; J. Antibiot. 71, 467 (2018)
- Bafilomycin C1 induces G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular cancer SMMC7721 cells: X. Gao, et al.; J. Antibiot. 71, 808 (2018)