Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
JaICA
Calcium Colorimetric Assay Kit (O-Cresolphthalein Method)

| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | Specific to Ca2+. |
| Crossreactivity | All |
| Quantity | Enough reagents for 200 tests. |
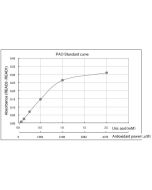
| Range | 0.2 - 30mg/dL |
| Sample Type |
Cell Lysate Plasma Saliva Serum Tissue Supernatant Urine |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Kit Contains |
1 x 38 ml R-1 Buffer (ready to use) 1 x 10 ml R-2 Chelate color (ready to use) 1 x 1.0 ml STD Calcium (Ca) standard 10mg/dL (ready to use) |
| Other Product Data |
This MC-Reagent Calcium Assay Kit is a direct colorimetric assay based on the O-Cresolphtalein (OCPC) method without deproteinization of the sample. The calcium determination is based on the reaction of calcium with O-Cresolphthalein complexone in alkaline solution, which yields a violet colored complex. The intensity of the color formed is proportional to the calcium concentration in the sample. Absorbance of the Ca2+-O-Cresolphtalein complex is measured at 570nm. Wavelength range of sensitivity: 560 ~ 590nm. Features of this Assay: Quick & Easy to use • Species independent • Highly sensitive, stable and suitable for high-throughput testing • No toxic substances • For cell lysates, serum, plasma and wide variety of biological samples |
| Declaration | Manufactured by JaICA. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | BLUE ICE |
| Short Term Storage | +4°C |
| Long Term Storage | +4°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Use/Stability | 12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Calcium is the most abundant mineral, essential for all living organisms, where Ca2+ sequestration and release into and out of the cytoplasm functions as a signal for many cellular processes. 99% is present as calcium hydroxyapatite in bones and less than 1 % is present in the extra-osseous ICS (intracellular space) or ECS (extracellular space), responsible for a myriad of important physiological effects. Calcium ion channels control the migration of calcium ions across cell membranes, permitting the activation and inhibition of a wide variety of enzymes. Calcium ions affect the contractility of the heart and the skeletal musculature and are essential for the function of the nervous system. In addition, calcium ions play an important role in blood clotting and bone mineralization. Abnormal calcium levels have been tied to neurological, endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, metabolic, and pulmonary diseases, as well as cancer. In plasma, calcium is bound to a considerable extent to proteins (approx. 40%), 10% is in the form of incorganic complexes and 50% is present as free (ionized) calcium. Clacium homeostasis is regulated by the parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitriol (CT) and calcitonin. Low levels of calcium are found in hypoparathyroidism, pseudohypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, malnutrition and intestinal malabsorbtion.
- Apoplastic mesophyll signals induce rapid stomatal responses to CO2 in Commelina communis: T. Fujita, et al.; New Phytol. 199, 395 (2013)
- Strawberry notch homologue 2 regulates osteoclast fusion by enhancing the expression of DC-STAMP: K. Maruyama, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 210, 1947 (2013)
- The pga gene cluster in Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is necessary for the development of natural competence in Ca(2+) -promoted biofilms: K. Hisano, et al.; Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 29, 79 (2014)