Cookie Policy: This site uses cookies to improve your experience. You can find out more about our use of cookies in our Privacy Policy. By continuing to browse this site you agree to our use of cookies.
JaICA
Total Antioxidant Capacity (PAO) Test Kit
As low as
813
CHF
CHF 813.00
In stock
Only %1 left
JAI-KPA-0501 KitCHF 813.00
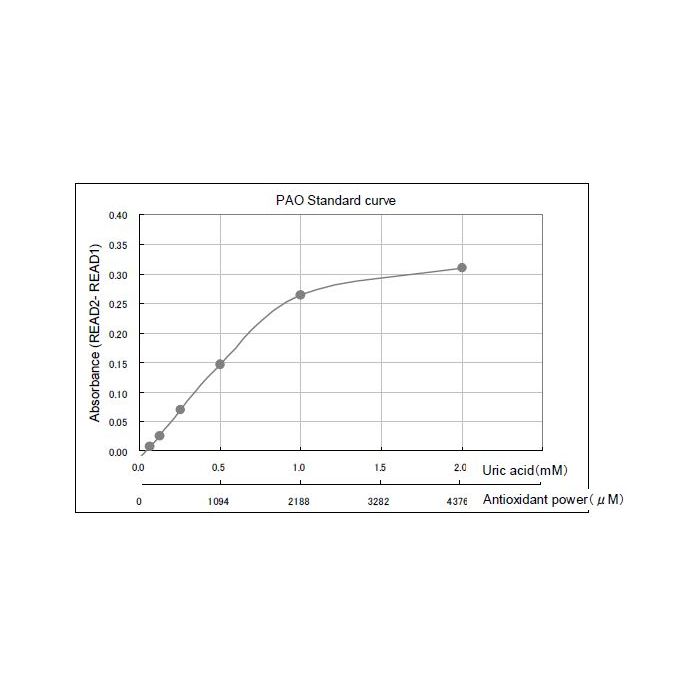
Figure 1: Standardcurve
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Product Type | Kit |
| Properties | |
| Application Set | Quantitative ELISA |
| Specificity | In the PAO assay kit, an easy and convenient method to measure antioxidant capacity is provided. Utilizing the reduction of cupric ion (Cu++ to Cu+), antioxidant capacity of samples can be detected in 5 minutes. Samples are mixed with Cu++ Solution. Cu++ are reduced by antioxidants to form Cu+. Reduced Cu+ react with Chromatic Solution (Bathocuproine), and can be detected by absorbance at wavelength 480 to 490 nm. Antioxidant capacity can be calculated from the Cu+ formed. PAO can detect not only hydrophilic antioxidants such as Vitamin C, glutathione, but also can detect hydrophobic antioxidants such as Vitamin E. Applicable for assessment of total antioxidants of serum, foods and beverage samples. |
| Crossreactivity |
All Human |
| Quantity | 96 wells |
| Range | 21.9 - 4378 μmol/L (cupric ion reducing power) |
| Sample Type |
Plasma Serum |
| Detection Type | Colorimetric |
| Declaration | Manufactured by JaICA. |
| Shipping and Handling | |
| Shipping | AMBIENT |
| Short Term Storage | +20°C |
| Long Term Storage | +20°C |
| Handling Advice | Do not freeze. |
| Documents | |
| Manual |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
| Product Specification Sheet | |
| Datasheet |
 Download PDF Download PDF |
Description
Oxidative stress plays on important role in various diseases and aging. The control of oxidative stress is expected to be useful to prevent diseases and aging.Oxidative stress is caused by the imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defense system. For accurate assessment of oxidative stress, measurement of ROS, oxidative damage and antioxidant activity may be essential. Recently, antioxidants as functional foods which scavenge ROS attract a great deal of attention.
Product References
- Restored Antioxidant Capacity Parallels the Immunologic and Virologic Improvement in Children with Perinatal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Receiving Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy: M. Martino, et al.; Clin. Immunol. 100, 82 (2001)
- Effect of epoetin on HO-1 mRNA level and plasma antioxidants in hemodialysis patients: L.A. Calo, et al.; Int. J. Clin. Ther. 41, 187 (2003)
- Oxidative stress-related factors in Bartter's and Gitelman9s syndrome: relevance for angiotensin IIsignalling: L.A. Calo, et al.; Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 18, 1518 (2003)
- Vitamin E-coated dialyzers reduce oxidative stress related proteins and markers in hemodialysis ? a molecular biological approach: L.A. Calo, et al.; Clin. Nephrol. 62, 355 (2004)
- Oxidative stress and its association with coronary artery disease and different atherogenic risk factors: C. Vassalle, et al.; J. Int. Med. 256, 308 (2004)
- Oxidative imbalance and cathepsin D changes as peripheral blood biomarkers of Alzheimer disease: A pilot study: E. Strafacea, et al.; FEBS Lett. 579, 2759 (2005)
- Antioxidant capacity as a reliable marker of stress in dairy calves transported by road: P. Pregel, et al.; Vet. Rec. 156, 53 (2005)